#'s
10-year rule
For years after 2020, with respect to inherited IRA accounts and retirement plans, beneficiaries subject to this rule must empty the entire account by the end of the 10th year following the year of the account owner's (or eligible designated beneficiary's) death. • Notice 2022-53 provides relief for beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule: The IRS will not treat a beneficiary of an inherited account in a plan or IRA who was subject to the 10-year rule and who failed to take an RMD for 2021 and 2022 as having failed to take the correct RMD. Retirement Topics - Beneficiary, irs.gov. • See eligible designated beneficiary.
18B attorney
In New York: An attorney given to a person by the court. County Law § 18b.
50/30/20 budget rule
"[S]pending 50% of our take-home pay on needs, 30% on wants and 20% on debt repayment and savings." Elizabeth Gravier, Here's how much money you should be investing in your 401(k), CNBC, July 30, 2023 (Apple News link).
60/40 portfolio
An investing portfolio made up of 60% stock and 40% bonds. • "For many years, a large percentage of financial planners and wealth managers crafted portfolios for their clients that were composed of 60% equities and 40% bonds or other fixed-income offerings. These so-called 'balanced portfolios' performed rather well throughout the ’80s and ’90s. The fixed income portion of the portfolio acted as a strong ballast for equities in both bull and bear markets." Caleb Silver, Ask the Experts: Is the 60/40 Portfolio Dead?, Investopedia (Apple News link).
401(k)
"[A]n employer-provided, defined contribution retirement plan. Employees can contribute either a fixed amount or a percentage of their paychecks to the plan to save for retirement. Some employers may match employee contributions up to a certain percentage." Olivia Peluso, Investing in a Retirement Plan for the First Time, Investopedia, June 2024 (Apple News link).
2503(c) trust
A trust for a minor where gifts for the minor child qualify for the gift tax annual exclusion if the child has to withdraw all of the trust assets at age 21. • Also called an "irrevocable minor's trust."
7520 rate
See Section 7520 interest rate.
A
abatement
The reduction of a gift under a will when the estate's assets cannot pay all of the gifts after paying the legal obligations of the estate.
abeyance
(1) Temporary suspension. • Example from Harbor Tech LLC v. Correa, 73 Misc.3s 1211(A), 2021 N.Y.Slip Op. 50995(U) (Kings Co. Civil Court Oct. 14, 2020, Stoller, J.): "ORDERED that the entirety of Petitioner's motion and the balance of Respondent Correa's cross-motion in Harbor Tech LLC v. Correa, Index # 60788/2019 (Civ. Ct. Kings Co.) remains in abeyance pending the stay of that proceeding . . . ."
(2) In property law, the opposite of vesting. • Black's Law Dictionary (10th Ed.) defines abeyance as "[a] lapse in succession during which no person is vested with title." • Example from Brennan v. Willson, 71 N.Y. 502 (1877): "Allen, J. By the assignment of the 2d of July, 1875, and the acceptance of the trust by the defendants and Trimble the assignees named therein, the property real and personal of the assignors, vested in the assignees in trust for the creditors. The title did not remain in the assignors, nor was it in abeyance awaiting the giving of security by the assignees as required by the statute, or the performance of any condition subsequent to the assignment. The creditors of the assignors acquired an interest in the assigned estate, and could enforce the execution of the trust."
abrogate
To repeal.
abstract fees
Expenses that a real estate buyer generally pays to research the property's title.
Accelerated Cost Recovery System (ACRS)
"The Accelerated Cost Recovery System (ACRS) applies to property first used before 1987. It is the name given for the tax rules that allow a taxpayer to recover through depreciation deductions the cost of property used in a trade or business or to produce income. These rules are mandatory and generally apply to tangible property placed in service after 1980 and before 1987. . . . ACRS consists of accelerated depreciation methods and an alternate ACRS method that could have been elected. The alternate ACRS method used a recovery percentage based on a modified straight line method." Instructions for Form 4562 (2019).
accidental American
"[A] person who has lived outside of the United States for the majority of their life but holds U.S. citizenship because they were born there." Kathleen Peddicord, Does Renouncing U.S. Citizenship Make Sense For The Average American Abroad?, Forbes, July 28, 2022 (Apple News link).
accounting period
NY EPTL 11-A-1.2 (Definitions): "(1) 'Accounting period' means a calendar year unless another twelve-month period is selected by a fiduciary. The term includes a portion of a calendar year or other twelve-month period that begins when an income interest begins or ends when an income interest ends."
accumulation planning
Planning that focuses on building wealth so an individual can have enough assets on which to retire. • Accumulation planning includes retirement planning and allocating assets between different classes of investments (such as bonds and stocks). Accumulation planning is performed by financial advisors, who typically invite the assistance of attorneys (to draft trusts and other estate planning instruments) and accountants (to prepare tax returns and assist with complex tax planning). See estate planning; c.f. decumulation.
acknowledgment
A legal statement that is signed before a person authorized to take such acknowledgment as a Notary Public, Commissioner of Deeds, Attorney, or Clerk of the Court. An acknowledgment verifies the identify of the person signing the statement.
acknowledgment of paternity
In New York: A written instrument authorized by the Social Services Law and Public Health Law whereby a person admits he is the biological father of a particular child. When properly executed and filed, the acknowledgment has the force and effect of an order of filiation.
action for mesne profits
See mesne profits.
action for the recovery of mesne profits
See mesne profits.
action of trespass for mesne profits
See mesne profits.
active trust
A trust in which the trustee has duties. C.f. passive trust.
activities of daily living (ADLs)
Basic personal tasks of everyday life: Bathing, dressing, toileting, transferring (walking), and continence.
ActivityPub
"[A] protocol that allows people across different platforms to follow, like and reply to one another." It’s time to bring back the open web., https://activitypub.ghost.org/.
ademption
When specifically bequeathed property fails because it is not owned by the testator at the time of the testator's death. The property could have been given to the beneficiary while the testator was alive, or it could have been sold, exchanged, lost, or otherwise disposed of before the testator died. • One court in New York gave this definition of ademption: The “extinction or withholding of some legacy in consequence of some act of the testator which, though not directly a revocation of the bequest, is considered in law as equivalent thereto, or indicative of an intention to revoke.” In re Dittrich, 53 Misc. 2d 782, 784, 279 N.Y.S.2d 657, 660 (Sur. Ct., Queens Co. 1967).
adjourn
To end the current meeting (such as a corporate meeting or court appearance) with the intention of resuming the meeting or case at a later time.
adjournment
The postponement of a court proceeding by a judge. • A judge can adjourn a case for the judge’s own reason or at the request of one of the parties to the case. The judge halts the proceeding and sets a date for the parties to return to court.
adjusted gross income (AGI)
"AGI stands for adjusted gross income, found on Line 11 of the 2023 Form 1040. AGI measures a filer’s income before Schedule A itemized deductions and tax credits, so it’s typically larger than taxable income on Line 15." Laura Saunders, To Lower Your Taxes in 2024, Make These Moves Now, WSJ, Dec. 29, 2023 (Apple News link).
administration
Proceeding of an estate of a person who dies without leaving a will (intestate).
administrator cum testamento annexo (c.t.a.)
An administrator c.t.a. (administrator cum testamento annexo; administrator with the will attached) is appointed to act as a personal representative in a probate proceeding in any one of three circumstances: (1) The will does not name an executor. (2) The will names an executor, does not name a successor executor, and the named executor cannot qualify as the executor of the estate. (3) The will names an executor, names a successor executor, and both the named executor and the successor executor cannot qualify as the executor of the estate. • Reasons executors (or successor executors) can fail to qualify include: (1) Refusing to accept the appointment, (2) dying before or during a probate proceeding, or (3) becoming mentally incapacitated before or during the probate proceeding. • An administrator c.t.a. to whom letters have been issued is an executor (SCPA 103(20)) and a fiduciary (SCPA 103(21)). • See executor, fiduciary.
administrator de bonis non (d.b.n.)
After an administration proceeding is commenced, an administrator d.b.n. (administrator de bonis non; administrator of goods not already administered) may be appointed to complete the administration of the estate if the administrator dies, resigns, becomes incapable of serving, or for any other reason is removed from office. See executor, fiduciary.
ad valorem tax
A tax that is based on the value of real property.
advance-and-protect strategy
An investment strategy that attempts to reduce risk by looking for investment opportunities to capture growth when the market is rising, but getting out of investments to protect principal when the market is falling. • Advance-and-protect strategy differs from the traditional diversification approach, which rides things out in rising and falling markets. It is touted to be good for retirees. See Jacqueline Sergeant, How One Firm Shields Retirees From Market Volatility, Financial Advisor, April 1, 2022 (reporting about Piershale Financial Group, who uses the advance-and-protect strategy and just "rotated to 100% cash for the time being").
affidavit
A written statement of facts made voluntarily and under oath.
affidavit of entitlement in Nevada
"In Nevada, the Affidavit of Entitlement process is governed by specific laws and regulations outlined in Chapter 146 of the Nevada Revised Statutes (NRS). . . . It establishes an individual’s right to inherit or receive property or assets from a deceased person’s estate when certain circumstances exist. An Affidavit of Entitlement is often utilized when the dead person did not leave a valid will or trust or when the assets in question are not subject to probate." Sean M. Tanko, What is the affidavit of entitlement in Nevada, seantankolaw.com, June 16, 2020.
affidavit of handwriting
A legal document that verifies the authenticity of a handwritten document or signature. The affidavit could come from a family member, a coworker, or anyone else who had regular correspondence with the person whose handwriting needs to be verified.
affirmative defense
“An affirmative defense is generally one in which a defendant has a burden of raising in the answer, and on which a defendant has a burden of proving at trial, unless in diversity cases applicable state law holds otherwise.” Thomas A. Mauet, Pretrial (Eighth Ed.).
after-tax dollars
Dollars on which a taxpayer was already taxed.
age-based 529 plan
"Age-based plans are geared towards investors who prefer a hands-off approach." Keith Reid-Cleveland & Patricia Oey, What Is a 529 College Savings Plan?, Morningstar, Nov. 2, 2022 (Apple News link). C.f. static 529 plan.
agency mortgage-backed securities
agency mortgage bonds
Bonds that "widely held by banks, insurers and bond funds because they are backed by the mortgage loans from government-owned lenders Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. The bonds are far less likely to default than most debt and are easy to buy and sell quickly . . . . But agency mortgage-backed securities, like all long-term bonds, are vulnerable to rising interest rates . . . ." Matt Wirz, Anxiety Strikes $8 Trillion Mortgage-Debt Market After SVB Collapse, WSJ, March 21, 2023 (Apple News link).
"aggregate" approach to partnership taxation
An approach to taxing the income of a partnership that treats the partnership as an aggregate of individuals, each conducting their share of the partnership's business. C.f. "entity" approach to partnership taxation.
Agreement Settling Account
See Receipt and Release Agreement.
aids
In feudal times, "originally financial contributions made to the lord by the tenant to assist the lord in times of emergency. . . . Aids were abolished in 1660." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 16 (7th ed. 2020).
alienable
Property that can be transferred during life.
alienation
The transfer of property to another, such as the transfer of title to real property to another. • Alienation can be voluntary or involuntary.
allodial
Ownership of real property without a service or duty owed to a lord; land held in absolute ownership. C.f. feudal. • In New York, since July 4, 1776, "all lands held under the authority of the state, shall be and remain allodial, and not feudal." Combs v. Jackson, 2 Wend. 153 (N.Y. 1828).
amend
To change.
American Citizens Abroad
A non-profit that focuses on issues that expats face. It advocates for the simplification of U.S. tax compliance for U.S. citizens abroad. https://www.americansabroad.org/
amortization
"Amortization is an accounting technique used to periodically lower the book value of a loan or an intangible asset over a set period of time. Concerning a loan, amortization focuses on spreading out loan payments over time. When applied to an asset, amortization is similar to depreciation." Amy Fontinelle, What Is an Amortization Schedule? How to Calculate with Formula, Investopedia, May 18, 2023.
annual compounding
"Annual compounding simply means that the returns in any one year are reinvested at the initial rate of return." Jonathan R. Macey, An Introduction to Modern Financial Theory (1991) at 4 n.6.
annuitant
The beneficiary of an annuity.
annuity
"An annuity is a yearly payment of a certain sum of money granted to another in fee for life or years." Dougherty v. Thompson, 167 N.Y. 472, 60 N.E. 760 (1901) (citations omitted). " . . . it is net and not gross income . . . ." Id. • "An annuity is an insurance contract that you can buy to provide a steady income like a pension, making it easier to plan for the uncertainty of life expectancy." Ashlea Ebeling, A Retirement Tax Break That Ends the Fear of Outliving Your 401(k), WSJ, July 23, 2023 (Apple News link).
answer
A pleading that states the defendant’s position to the case.
antenuptial agreement
A couple's agreement respecting their property that they make before they marry, which governs the division of their property upon their divorce.
appellant
A party who appeals and wants to reverse a lower court's decision or order. • Archaically, another word for appellant was "plaintiff in error." • C.f. appellee.
appellee
In a case that is being appealed, the prevailing party in a lower court that must now respond to an appeal, seeking to affirm the lower court's decision. • Archaically, another word for appellant was "defendant in error." • C.f. appellant.
appraisal gap
"Appraisal gaps . . . arise when homes appraise for less than the contract price. They often occur in tight markets where buyers have to bid above the asking price to secure a home." Robyn A. Friedman, Waiving the Appraisal Gap Can be Both a Bargaining Chip and Big-Time Risk for Home Buyers, WSJ, Sept. 3, 2023 (Apple News link).
appraisal gap waiver
"Waiving the appraisal gap simply means that a buyer will move ahead with the purchase at the agreed-upon price no matter what the appraised value of the home. . . . Although real-estate agents often refer to 'appraisal waivers,' in most states, there is in fact no appraisal contingency in a standard home-purchase agreement. Instead, the issue arises in the context of the mortgage contingency because a lender’s mortgage commitment is conditioned upon receipt of a satisfactory appraisal. If the appraisal comes in for at least the purchase price, the deal proceeds as planned. If it comes in too low, however, that will affect the loan-to-value ratio used by a lender to qualify the buyer—and often results in the lender approving a lower mortgage amount." Robyn A. Friedman, Waiving the Appraisal Gap Can be Both a Bargaining Chip and Big-Time Risk for Home Buyers, WSJ, Sept. 3, 2023 (Apple News link).
appraisal waiver
See appraisal gap waiver.
artificial intelligence (AI)
The simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. One of the many applications of AI is generating automated content, which involves using algorithms and machine learning techniques to automatically create text, images, videos, and other forms of content. This capability of AI can be useful in a variety of industries, such as marketing, journalism, and e-commerce, where there is a need for large quantities of content to be produced quickly and efficiently. See Artificial Intelligence, Pro Epic Technology Solutions.
asset allocation
The strategic choice of assets by a trustee to control the income that an income beneficiary obtains. • "Asset Allocation involves a choice among two or more asset classes, most or all of which are risky. In practice, emphasis is often placed on the selection of an appropriate mix of stocks and risky bonds." W. Sharpe, Investments 663 (3d ed. 1985), qtd in Joel C. Dobris, Probate World at the End of the Century: Is a New Principal and Income Act in Your Future, 48 Rec. Ass'n B. City N.Y. 280 (1993).
asset protection
Planning that shields assets from plaintiffs, ex-spouses, and other creditors. • See estate planning.
assignee for the benefit of creditors
"[A]n alternative to formal bankruptcy proceedings, in which a third party executes a company’s liquidation. The American Bar Association calls the move an 'advantageous and graceful exit strategy.'" Luke Fortney & Emma Orlow, One of Brooklyn's Newest Food Halls Shutters With 'Zero Notice' After Four Months, Eater New York, March 30, 2023 (Apple News link).
autophagy
"[T]he removal of damaged cells . . . ." Ashlee Vance, The Most Secretive Longevity Lab Finally Opens Its Doors, Bloomberg Businessweek, Dec. 19, 2023 (Apple News link).
average liquidity coverage ratio
"[A] key measure of how much cash-like assets [a] bank has . . . ." John O'Donnell & Andres Gonzalez, Switzerland's secretive Credit Suisse rescue rocks global finance, Reuters, March 20, 2023 (Apple News link).
B
baby boomer
Baby boomers are individuals born between 1946 and 1964, characterized by a significant increase in birth rates following World War II.
back-end SLAT
"[I]t is basically a high grade traditional life insurance trust . . . that gives the person setting it up . . . an extra shot at getting access to the money in the trust." Martin Shenkman, Back End Slats -- A SLAT, ILIT, DAPT, OR SPAT By Another Name?, Forbes, March 12, 2023 (Apple News link).
backfire effect
A psychological phenomenon in which attempts to correct misinformation inadvertently strengthen the original false belief, particularly among individuals whose identities or worldviews are closely tied to the misinformation.
balanced portfolio
See 60/40 portfolio.
Barista FIRE
"The [FIRE] movement even has offshoots, with some focusing on extreme frugality and others on building a large retirement fund or keeping a part-time job. . . . There is Barista FIRE, representing semi-retirees who maintain income-generating hustles because they haven't saved enough to live entirely off a retirement fund." Laila Maidan & Kathleen Elkins, FIRE Movement: Early retirees discuss limitation, need to resume working, Business Insider, Sept. 13, 2023 (Apple News link). • See financial independence and FIRE movement; c.f. Fat FIRE and Lean FIRE.
basis point
A unit of measure in finance that is used to describe a percentage change or rate change. One hundred basis points is equal to one percent. One basis point is equal to 0.01% (1/100th of a percent, which is 0.0001 in decimals). • Example: "The financial shock delivered by the banking ferment is tantamount to "50 basis points [that is, one half of a percentage point] of policy tightening," Joseph Brusuelas, chief economist at the consulting firm RSM, wrote Tuesday." Michael Hiltzik, Column: The Fed's anti-inflation work is almost done, with an assist from the banking crisis, Los Angeles Times, March 22, 2023 (Apple News link).
Battle of Hastings
A battle in 1066 in which William the Duke of Normandy defeated the Anglo-Saxon King, Harold II, and became King of England.
bear market
A "grizzly decline" of a widely-followed index, such as the Dow or S&P 500, of at least 20% from a recent peak. Caitlin Ostroff, The Dow Is Officially in a Bear Market. Here's What to Know., WSJ, Sept. 26, 2022 (Apple News link) ("There is nothing official about the determination. The designation is a shorthand way for Wall Street to mark when markets have taken a tumble."). • "The tech-focused Nasdaq plunged 10% and into a bear market, meaning the index had fallen 20% from its previous high." Vicky Ge Huang, Krystal Hur & Gunjan Banerji, Trump’s Tariffs Wipe Out Over $6 Trillion on Wall Street in Epic Two-Day Rout, WSJ, April 4, 2025 (Apple Ness link). • C.f. bull market, correction.
bench trial
A trial by a judge, as opposed to a trial by jury.
beneficiary
(1) Generally: A person who is designated to receive a distribution under a will or trust, the proceeds of an insurance policy or a retirement account, or the benefits from financial producs. Beneficiaries can be primary or contingent. • "A beneficiary is the person or entity that you legally designate to receive the benefits from your financial products." Naming a beneficiary: What you need to know, Securian Financial. • "A beneficiary is a person or entity legally designated to receive the benefits or proceeds of a trust, will, insurance policy or retirement account." Entrepreneur Staff, What Is a Beneficiary? Here's Everything to Know., Entrepreneur, Feb. 24, 2023 (Apple News link).
(2) Estate adminsistration: A person who is entitled to some or all of an estate. • NY EPTL § 11-A-1.2 (Definitions): "(2) 'Beneficiary' includes, in the case of a decedent's estate, a distributee and testamentary beneficiary . . . ." • NY SCPA 103(8): "Any person entitled to any part or all of an estate."
(3) Trusts: Income and remainder beneficiaries. • NY EPTL § 11-A-1.2 (Definitions): "(2) 'Beneficiary' includes, . . . in the case of a trust, an income beneficiary and a remainder beneficiary."
beneficiary form
"[A] registration of a security which indicates the present owner of the security and the intention of the owner regarding the person who will become the owner of the security upon the death of the owner." NY EPTL 13-4.1(a).
bequest
(1) Broadly, the transfer of property by any arrangement or procedure at death.
(2) Narrowly, a transfer of property by will. • Usually, a "bequest" refers to the transfer of personal property by will. For example, NY SCPA 103(9) defines a bequest as "[a] transfer of personal property by will." • Bequest can also be used to refer to the transfer of any property by will, so it can also include and refer to the transfer of real property by will.
bias
"Systematic errors are known as biases, and they recur predictably in particular circumstances." Daniel Kahneman, Thinking, Fast and Slow 3 (2011).See normalcy bias, persistence bias, projection bias, and status quot bias.
bill jacket
"A bill jacket is a compilation of documents received by the Governor's Office of General Counsel after a New York bill has passed both houses of the legislature and is awaiting the governor's signature. The bill jacket may contain letters and memoranda from state agencies, legislators, lobbyists, bar associations and private citizens discusssing the pros and cons of a bill and why the governor should (or should not) sign the bill." New York State Legislative History Research: Bill Jackets, Brooklyn Law School.
Billionaire Minimum Income Tax
A tax proposed by President Biden on households worth at least $100 million. It is a 20% levy on all income and unrealized appreciation on investments. See Hani Sarji, Biden Proposes Billionaire Minimum Income Tax in 2023 Budget, But It's a Gimmick, Wills, Trusts, Estates, April 12, 2022.
blended family
A family where parents have children from previous marriages.
bond
"[A] bond is a loan an investor makes to a borrower—typically a company or a government agency—that uses the money to fund its operations. If you’re the investor, you receive regular interest payments on the loan; that’s why bonds are called fixed-income investments. A bond has a maturity, or term, which is the amount of time over which it is scheduled to make payments. When the bond reaches maturity, the loan amount, or principal, is returned to you, the investor." Penelope Wang, 8 Things You Need to Know About Bonds, AARP Bulletin, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link).
bond ladder
book value of a bond
The amount that an investor paid for a bond. C.f. market value of a bond.
"boomerang children"
Children "who leave and return a few times, occasionally staying until the death of the last parent." Andrew Auerbach & Jean Blacklock, ‘Boomerang children’ are a newer part of the financial planning conversation, Globe and Mail, June 20, 2024 (Apple News link).
borough English tenure
See burgage tenure.
boundary line agreement
A means of resolving a dispute over the boundary line between properties. This agreement avoids litigation to determine the exact boundary of properties.
broker
Someone paid to facilitate the buying and selling of an asset, such as real estate or stocks and bonds. Brokers do not have a fiduciary duty to their clients.
brokering fractional shares in life insurance
Buying life insurance "policies from owners who can no longer afford to pay the premiums and selling the policies in fractional shares to investors." Kevin Brodehl, "Equitable Buyout" as a Remedy for LLC Wrongdoing?, JD Supra, June 26, 2023.
brownfield site
Land that was previously used for industrial or commercial purposes and that may be contaminated by toxic waste. • A brownfield site is sometimes simply called a "brownfield."
BRRRR strategy
BRRRR stands for "buy, rehab, rent, refinance, and repeat." "It involves buying and flipping a distressed property, renting it out, and then doing a cash-out refinance on the property so you have the funds to buy another property and repeat the process." Kathleen Elkins, How to use HELOC home equity line of credit buy property build wealth, Business Insider, Oct. 13, 2022 (Apple News link).
bull market
An increase of a widely-followed index, such as the Dow or S&P 500, of at least 20% from a recent low. C.f. bear market , correction.
burgage tenure
In feudal times, a type of socage tenure that prevailed in some places by custom that provided that on the death of an owner, land descended to the youngest son. • Also known as "borough English tenure." C.f. gavelkind tenure, primogeniture.
burial insurance
"This type of insurance helps prevent the burden of final expenses from falling on the shoulders of your loved ones. It’s a major part of most life insurance policies, but you can also purchase it as a solo policy. . . . Simply put, burial insurance is used to pay for your funeral, burial and grave. It is a smaller, less comprehensive form of life insurance that’s generally easier to get but usually offers a smaller death benefit." Jacob Clifton, What Is Burial Insurance?, Money (Apple News link). • Burial insurance is also called "funeral insurance" and "final expense insurance."
bylaws
An internal corporate document that contains the rules for the corporation for such things as meetings and voting. • Bylaws of a corporation are “internal” because they are not filed with the state.
C
cabined
(1) Literal meaning: To be enclosed within a cabin or a small, confined space. (2) Figurative use: To limit or restrict something within a certain boundary or scope. In writing, especially legal writing, it is used to indicate that a principle or rule is applied within a narrow or specific context. Example: "[S]uch deferential review, which the Court was far from consistent in applying, was cabined to factbound determinations." Loper Bright Enterprises et al. v. Raimondo, Sec’y of Commerce, et al., 603 U. S. ____ (2024).
California source income
Income that is subject to California income taxation regardless of the residence of a trust's fiduciaries and beneficiaries. "Examples of California source income include rental income or any other type of income derived from the ownership, control, or management of real or tangible personal property within California, gains realized from the sale of such property, income from a trade or business conducted within California, and income from certain intangible personal property." Eric Bardwell, California Admits Incomplete Gift Non-Grantor Trusts Work...For Now, Bloomberg Tax, Dec. 3, 2020.
call
(1) A financial contract that gives an investor the ability to buy an asset for a set price. • A call is a bet that the asset will trade higher. So, it is considered a bullish contract. • C.f. put.
(2) A type of financial contract that allows a borrower to pay back its debt before the agreed upon maturity debt. See callabale bond and [callable certificate of deposit].
callable bond
A bond that allows the borrower repay the principal before the previously agreed upon maturidy date. See call.
callable certificate of deposit
A callable certificate of deposit is a certificate of deposit (CD) that allows the issuer (not the purchaser) to redeem the CD after a specified period of time. • The issuer is likely to redeem the certificate of deposit when interest rates decline. The purchaser's CD could end upon maturity, upon redemption by the issuer, or upon the purchaser's sale of the CD on the secondary market. Like all CDs, a callable certificate of deposit presents a significant lock-in risk to purchasers who might need the funds prior to maturity. See call; Hani Sarji, What Is a Callable Certificate of Deposit?, Wills, Trusts, Estates, April 2, 2022.
capital flight
Rich people migrating to other jurisdictions in response to higher taxes, resulting in lower tax revenue for the tax jurisdiction. See Selwyn Duke, Soak the Rich? Or Should Wealth-tax Advocates Soak Their Heads?, The New American, July 1, 2023 ("[E]ver since Norway's Labor Party won power in 2021 and kept its promise to increase the nation's wealth tax, the Scandinavian country's rich have been leaving -- taking tens of billions of dollars with them. . . .).
capital gains
Gains from the sale of an asset, such as a real estate, stocks, an index fund, or cryptocurrency. • "Capital gains are the difference between sale price and cost basis, and investors face federal taxes of up to 23.8%." Richard Rubin & Paul Kiernan, U.S. Tackles Crypto Tax Mess, WSJ, Aug. 25, 2023 (Apple News link).
capital gains tax
A tax on the sale of an asset (such as a real estate, stocks, an index fund, or cryptocurrency).
capital loss
A loss from the sale of an asset for less than its purchase price.
caption
What is written at the top of all court papers. It says things like the names of the parties, court, and case number.
casual ejector
The defendant in an ejectment action. This person may not be the actual person who physically removed the lawful possessor from the property but is named as a defendant in an ejectment action due to a legal fiction that assumes that they were the ejector. • See ejector.
catch and kill
A publication's purchase of a story (the "catch") in order to prevent its publication (the "kill"). • "The publisher of the National Enquirer, a longtime ally of Mr. Trump, bought Karen McDougal's story for $150,000 in August 2016 to take it off the market and prevent her from telling it elsewhere, at tabloid practice known as 'catch and kill.'" Corinne Ramey & Joe Palazzolo, Grand Jury Votes to Indict Donald Trump, WSJ, March 30, 2023 (Apple News link).
catch-up contribution
If permitted by a 401(k), 403(b), governmental 457(b), SARSEP or SIMPLE IRA plan, participants who are age 50 or over at the end of the calendar year can also make catch-up elective deferral contributions beyond the basic limit on elective deferrals. • Employees 50 or older can save extra money into their 401k). For 2023, eligible employees can save an additional $7,500 after maxing out their deferrals at $22,500. Starting 2024, 401(k) catch-up contributions can only be made to after-tax Roth accounts. Starting in 2025, employees 60 to 63 years old can contribute 50% more. See Kate Dore, This lesser-known 401(k) plan change will soon strip higher earners of a tax break, CNBC, July 21, 2023 (Apple News link). • See elective deferral contributions.
CD ladder
"Creating a CD ladder, where you buy several smaller CDs that mature at different intervals instead of one large CD, can help you increase liquidity and avoid or minimize early withdrawal penalties." • See
certificate of deposit. Amy Fontinelle, Put Your Emergency Fund to Work, Investopedia, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link).
cell reprogramming
"[A] process, proven out in numerous animal experiments, in which the cells of an older creature can be treated with a combination of proteins or molecules and turned into much younger cells. Based on Nobel Prize-winning science, it’s something Retro and a handful of other startups consider the most promising longevity technology to yet appear." Ashlee Vance, The Most Secretive Longevity Lab Finally Opens Its Doors, Bloomberg Businessweek, Dec. 19, 2023 (Apple News link).
certificate of deposit
An account with a fixed term (e.g., six months or two years) that pays the account holder the principal plus accrued interest by the end of the term. • "CDs are similar to bonds but come with protection from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. for deposits amounts of $250,000 or less per account per bank." Mitchell Martin, How Bond Laddering Can Keep You From Having An SVB Portfolio, Forbes, April 8, 2023 (Apple News link).
certified financial planner (CFP)
A financial adviser who has passed an exam, provides financial advice and planning based, and owes clients a fiduciary duty. • "Consumers should understand that a CFP professional describing themselves as a fiduciary is describing a professional standard of fiduciary care and not a legal standard of fiduciary care. On the other hand, registered investment advisers (RIAs) are registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission or a state’s security agency and are therefore legally bound to the fiduciary role." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
cestui que trust
A beneficiary of a trust.
chattel
Personal property that is a physical object that is typically movable or transferable; not real property. • Thomas Blount, A Law-Dictionary and Glossary (1717) defines chattels (with citations omitted):
Chattels, or Catals, (Catalla,) comprehend all Goods moveable and immoveable, except such as are in Nature of Freehold, or Parecel of it, as may be collected out of Staundf. Chattels are either Personal or Real. Personal, may be so called in two Respects: One, because they belong immediately to the Person of a Man, as a Bow, Horse, etc. The other, for that being any Way injuriously withheld from us, we have no Means to recover them, but Personal Actions. Chattels Real, are such as either appertain not immediately to the Person, but to some other Thing, by way of Dependency, as a Box with Charters of Land, Apples upon a Tree, or a Tree it self growing on the Ground. ... [O]r such as are issuing out of some immoveable Thing to a Person, as a Lease or Rent for Term of Years.
Chevron deference
"On Tuesday, a Supreme Court precedent bolstering federal agencies’ ability to regulate wide aspects of American life will mark its 40th anniversary. . . . The doctrine, known as Chevron deference, requires courts to accept agencies’ reasonable interpretations of federal laws when they are ambiguous. // Presidential administrations have invoked it to uphold regulations from fishing boats to cryptocurrency to environmental protections." Zach Schonfeld & Ella Lee, Supreme Court opinion season nears climax: 5 major decisions to come, The Hill, June 23, 2024 (Apple News link).
chose
Thing.
chose in action
"Chose in Action is a Thing incorporeal, and only a Right; as an Annuity, Obligation for Debt, a Covenant, Voucher by Warranty, and generally all Causes of Suit for any Debt or Duty, Trespas for Wrong, are to be accounted Choses in Action. And it seems Chose in Action may be also called Chose in Suspence; because it has no real Existence or Being, nor can properly be said to be in our Possession." Thomas Blount, A Law-Dictionary and Glossary (1717).
chosen family
In the LGBTQ+ community and for other marginalized groups, "the idea that [f]amily -- for the purposes of emotion and physical support, living accommodations, etc. -- doesn't have to be biological. Your chosen family may include a romantic partner or any number of close platonic relationships." Kamaron McNair, Take 3 steps to protect your assets if you're LGBTQ, say experts: This is 'our first recommendation to every couple', CNBC, June 28, 2023 (Apple News link). "Chosen families are common in the LGBTQ community because so many members have been ostracized or completely cut off from their biological families due to their gender or sexual identity."
codicil
An amendment to a previously executed will. • A codicil can add to, modify, or revoke parts of a will. NY EPTL 1-2.1. It can confirm the will in whole or in part by republication. Id. But a codicil cannot revoke the entire will. Id. A codicil must be executed with the same formalities as a will (which are set forth in EPTL 3-2.1) because the term “will” generally includes a “codicil.” EPTL 1-2.19(b).
cognovit judgment
A confession of judgment by a debtor. • "The cognovit is a contractual provision, employed as a security device, whereby the obligor consents in advance to the creditor’s obtaining a judgment without notice or hearing (see, Overmyer Co. v. Frick Co., 405 U.S., at 176, 92 S.Ct., at 777-78, supra). In the present case, the cognovit contained a “warrant of attorney,” a provision that empowers any attorney to enter the obligor’s appearance in any court of record and to waive — on the obligor’s behalf — process and consent to the entry of judgment (Atlas Credit Corp. v. Ezrine, 25 N.Y.2d, at 225, 303 N.Y.S.2d 382, 250 N.E.2d 474, supra)." Fiore v. Oakwood Plaza Shopping Center, 78 N.Y.2d 572 (affording full faith and credit to a Pennsylvania cognovit of judgment).
coins
"Units of cryptocurrency are generally referred to as coins or tokens." Rev. Rul. 2023-14. See cryptocurrency.
collateralized debt obligation (CDO)
An asset-backed security created by bundling a variety of revenue-generating assets (known as the "collateral" or "underlying assets"). These assets are transferred to a special purpose entity, which then issues debt securities backed by the income generated by the assets. A CDO is typically governed by an indenture, and the granting clause in the indenture transfers all right, title, and interest in the collateral debt securities to the trustee for the benefit and security of the secured parties.
collateral heirs
Cousins, nieces, nephews, uncles, and aunts.
combined loan-to-value ratio (CLTV)
For real estate owners who already have a mortgage on a home but are looking for a second mortgage or a home equity line of credit, this ratio adds the existing mortgage and the proposed mortgage and divides it by the value of the property. • "Let’s say you have an outstanding balance of $250,000 on a home that is appraised at $500,000, and you want to borrow $30,000 in a home equity line of credit (HELOC) to pay for a kitchen renovation. Here’s a simple breakdown of the combined LTV ratio: $280,000 ($250,000 + $30,000) / $500,000 = 56 percent CLTV." David McMillin, What is a loan-to-value ratio?, Bankrate, June 27, 2023 (Apple News link). • See loan-to-value ratio.
Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget
A nonpartisan, non-profit organization that educates the public and policymakers on issues with significant fiscal policy impact and advocates for fiscal responsibility. https://www.crfb.org/
common law
"[S]uch Laws as were generally taken and holden for Law, before any Statute was made to alter the same; as, neither Tenant for Life, nor for Years, were punishable by the Common Law for doing Waste till the Statute of Clou. can. 5 was made, which gives Action of Waste against them: But Tenant by Courtesy, and Tenant in Dower, were punishable for it before the said Statute." Thomas Blount, A Law-Dictionary and Glossary (1717).
community property
"[A] system of marital property rights derived from the Spanish law and exists in eight states: Arizona, California, Idaho, Louisiana, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas and Washington. Under this system husband and wife are co-owners of all real and personal property acquired by either or both during the marriage other than by gift, bequest, devise or inheritance." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 309 n.1 (7th ed. 2020).
community spouse
For purposes of Medicaid, the spouse who does not need long-term or nursing home care. This spouse continues to live in the community.
commute
To change the type of obligation or payment. • Example: "When the practice of retaining hired servants developed in the fourteenth century, the services due from serjeanty tenants were, in many cases, commuted to a payment of rent, and the tenure was converted into socage." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 11 (7th ed. 2020) (emphasis added).
compound interest
"[T]he interest on savings calculated on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest from previous periods. . . . Compounding multiplies money at an accelerated rate, and the greater the number of compounding periods, the greater the amount of compound interest." Jason Fernando, The Power of Compound Interest, Investopedia, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link). • "Compounding, as in compound interest, is when you earn interest on both the money you've saved and the interest you earn on that money saved. As time passes, your interest will accumulate more rapidly and snowball. This can have a significant impact on your savings over time." Olivia Peluso, Investing in a Retirement Plan for the First Time, Investopedia, June 2024 (Apple News link).
concurrent interest
See concurrent ownership.
concurrent jurisdiction
Two or more courts having the same power to hear a case.
concurrent ownership
Two or more persons owning an interest in the same property. • Generally, concurrent interests are classified as tenancy in common, joint tenancy, joint tenancy with right of survivorship, or tenancy by the entirety. Two additional classifications of co-ownership are community property and tenancy in partnership. • See NY EPTL Article 6 Part 2 (Estates Classified As to Number of Persons), NY EPTL 6-2.1 (Estates in severalty, joint tenancy, tenancy by the entirety and in common).
conflict of laws
Occurs when different jurisdictions’ laws apply to a case, creating uncertainty about which legal principles should govern the outcome. This often involves determining which jurisdiction’s laws are most appropriate to resolve the dispute. • See 📋 New York Conflict of Laws in the Outline.
Congressional Review Act (CRA)
Procedures that allow Congress to overturn rules issued by federal agencies. • The Congressional Review Act (CRA): Frequently Asked Questions, Congressional Research Service, Nov. 12, 2021:
The Congressional Review Act (CRA) is a tool that Congress may use to overturn rules issued by federal agencies. The CRA was included as part of the Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Fairness Act (SBREFA), which was signed into law on March 29, 1996. The CRA requires agencies to report on their rulemaking activities to Congress and provides Congress with a special set of procedures under which to consider legislation to overturn those rules.
Under the CRA, before a rule can take effect, an agency must submit a report to each house of Congress and the comptroller general containing a copy of the rule; a concise general statement describing the rule, including whether it is a major rule; and the proposed effective date of the rule. After receiving the report, Members of Congress have specified time periods during which they must submit and act on a joint resolution of disapproval to take advantage of the CRA’s special “fast track” procedures. If both houses pass the resolution, it is sent to the President for signature or veto. If the President were to veto the resolution, Congress could vote to override the veto.
If a joint resolution of disapproval is submitted within the CRA-specified deadline, passed by Congress, and signed by the President, the CRA states that the disapproved rule “shall not take effect (or continue).” The rule would be deemed not to have had any effect at any time, and even provisions that had become effective would be retroactively negated.
Furthermore, if a joint resolution of disapproval is enacted, the CRA provides that a rule may not be issued in “substantially the same form” as the disapproved rule unless it is specifically authorized by a subsequent law. The CRA does not define what would constitute a rule that is “substantially the same” as a nullified rule. Additionally, the statute prohibits judicial review of any “determination, finding, action, or omission under” the CRA.
Since its enactment, the CRA has been used to overturn a total of 20 rules: 1 in the 107 th Congress (2001-2002), 16 in the 115 th Congress (2017-2018), and 3 in the 117 th Congress (2021-2022).
In January 2022, House Republicans passed a measure (H.J.Res.7) ending the coronavirus national emergency under the Congressional Review Act (in a 229-197 vote), then the Senate passed the measure in April 2022 (in a 68-23 vote), and then President Biden signed the resolution, instead of vetoing it. Azi Paybarah, Biden signs resolution ending coronavirus national emergency, Washington Post, April 10, 2023 (Apple News link) (stating, "Despite Biden telling Congress in January that he would end the health emergency in May, House Republicans passed the measure ending the national emergency under the Congressional Review Act, which allows Congress to overturn rules by federal agencies via a simple majority vote."); Ali Zastav, Phil Mattingly & Manu Raju, Senate votes to end Covid-19 emergency, 3 years after initial declaration, CNN, March 29, 2023 (stating, "The measure was able to succeed in the Senate by a simple majority through the Congressional Review Act, which allows a vote to repeal regulations from the executive branch without breaking a filibuster at a 60-vote threshold that is required for most legislation in the chamber.)".
consideration
Something of value, such as money.
constructive fraud
"It is a well-settled rule that " 'fraud vitiates all contracts, but as a general thing it is not presumed but must be proved by the party seeking to [be] relieve[d] . . . from an obligation on that ground' " (Matter of Gordon v Bialystoker Ctr. & Bikur Cholim, 45 NY2d 692, 698 [1978], quoting Cowee v Cornell, 75 NY 91, 99 [1878]). However, an exception to that general rule provides that where a fiduciary relationship exists between the parties, the law of constructive fraud will operate to shift the burden to the party seeking to uphold the transaction to demonstrate the absence of fraud (see Matter of Greiff, 92 NY2d 341, 345 [1998]). . . . We have applied the constructive fraud doctrine in different contexts, but in each one, the pertinent factor present is that the fiduciary stood to benefit from the transaction itself." Aoki v. Aoki, 27 N.Y.3d 32, 39, 49 N.E.3d 1156, 1160, 29 N.Y.S.3d 864, 868 (2016).
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
"[M]easures inflation by tracking the changes in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services over time. These goods and services include food and beverages, housing, apparel, transportation, medical care, recreation, education, and communication." Robert C. Kelly, Is the Consumer Price Index the Best Measure of Inflation?, Investopedia, Sept. 12, 2023 (Apple News link).
contingent convertible bond (CoCo)
Bonds that "are mainly issued by European and Asian banks, but bought by investors all over the world. Cocos help banks deal with heavy losses because in times of stress they convert to equity or are written down. They become risky in sudden and unexpected ways." Paul J. Davies, Investors Diving Into Risky Bank Bonds, WSJ, Dec. 26, 2017 (Apple News link). • See Matt Wirz & Caitlin McCabe, Credit Suisse Bond-Wipeout Threatens $250 Billion Market, WSJ, March 20, 2023 (Apple News link) ("Deal would write down more than $17 billion of the bank's riskiest bonds. . . . The complete write-off by Credit Suisse, one of the largest issuers in the AT1 market, will likely hurt investor appetite for the bonds . . . Ultimately, AT1 bonds will become more expensive for banks to issue, reducing their ability to make new loans . . . .").
continuously compounding interest
"Some banks also offer something called continuously compounding interest, which adds interest to the principal at every possible instant. For practical purposes, it doesn’t accrue that much more than daily compounding interest unless you want to put money into an account and take it out on the same day." Jason Fernando, The Power of Compound Interest, Investopedia, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link).
contractual buyout
For an LLC: "where the operating agreement provides a buyout mechanism." Kevin Brodehl, "Equitable Buyout" as a Remedy for LLC Wrongdoing?, JD Supra, June 26, 2023. C.f. equitable buyout, statutory buyout.
contractual will
"[E]ach spouse agrees that the surviving spouse doesn't have the legal right to execute a new will that cuts out the children of the deceased spouse." Debbie Carlson, A Will Can Split a Family. How to Avoid the Hurt., Barron's, July 15, 2023 (Apple News link). • A contractual will may be useful in blended families.
contribution
The amount an employer and employees (including self-employed individuals) pay into a retirement plan.
convenience of employer rule
An exception to the general rule that an employee pays taxes in the jurisdiction in which the employee physically performs services. Under the "convenience of employer rule," if an employee works from home through the employer's necessity, then the employee will be taxed in the employee's home location; but if the employee works from home for the employee's own convenience, then the employee's wages for those workdays are classified as if the employee was working from the employer's physical office. See N.Y. Dept. of Tax. & Finance TSB-M-06(5)I. • The "convenience of the employer rule" can cause an employee to be taxed in the state where an employer's physical office is located even though the employee is a non-resident of the taxing state and does not physically work in that state.
convertible bond
A type of bond that can be exchanged for a certain number of shares of the company that issued it. This gives the bondholder the option to benefit from the company's stock performance, while also receiving regular interest payments from the bond. A convertible bond usually has a lower interest rate than a regular bond, because of the conversion feature. A convertible bond can be converted at specific times during its life, and usually at the bondholder's discretion.
{Id: copyhold-tenure}
copyhold tenure
See villein.
corporate bond
A bond that is issued by a company.
correction
A decline of a widely-followed index, such as the Dow or S&P 500, of at least 10% from a recent low. C.f. bear market, bull market.
correction deed
Corrects a prior deed in a chain of title, such as a name that is misspelled.
cost basis
How much a taxpayer pays for an asset.
cost of living
"Cost of living is a measure of how expensive it is to live in a particular place at a particular time based on how much things like rent, gas, and food cost." Jeremy Salvucci, What Is Cost of Living? Definition, Examples & Importance, TheStreet, June 13, 2022 (Apple News link).
court
A tribunal presided over by a judge.
Court Baron
In feudal England, a lord's manorial court for free tenants. C.f. Court Customary.
Court Customary
In feudal England, a lord's manorial court for villein tenants. C.f. Court Baron.
covenant of seisin
Edward T. Reilly, The Covenant of Seisin, St. John's Law Review, Vol. 10, Dec. 1935:
[A]mong many things, the usual warranty deed embraces an undertaking on the part of the grantor that he is seised as owner, at the time of the grant, of the land which the deed purports to convey. This assurance to the purchaser that the covenantor is possessed of the very estate in quantity and quality which his conveyance intends to transfer is called the "covenant of or for seisin."
The covenant need be couched in no particular terms; it need merely be but a stipulation or declaration that the grantor is seised of an estate of the quantum which he undertakes to convey. The New York short form of deed, culled mainly from the fuller language of former deeds, simply words this covenant for title as follows: "That the party of the first part is seised of said premises in fee simple * * *." . . .
covenant for seisin
See covenant of seisin.
Coverdell education savings account (Coverdell ESA)
"[A] trust or custodial account set up in the United States solely for paying qualified education expenses for the designated beneficiary of the account. This benefit applies not only to qualified higher education expenses, but also to qualified elementary and secondary education expenses." Topic No. 310, Coverdell Education Savings Accounts, IRS.
CPLR § 408
In New York, "[d]iscovery in special proceedings is not as broad as in other civil proceedings. CPLR 408 governs discovery in special proceedings and requires leave of court for any disclosure with certain exceptions . . . ." Matter of K.Z. v. P.M., 29 Misc. 3d 572, 2010 NY Slip Op 20335 (Family Court Orange Co. 2010). • Failing to obtain leave of court for disclosure can be used to challenge a discovery subpoena in special proceedings (such as landlord and tenant summary proceedings). Example: "In reply to Respondent Soto's opposition that Petitioner did not satisfy the elements necessary for leave to obtain discovery pursuant to CPLR §408, Petitioner's counsel affirms, inter alia, that the subpoena is a trial subpoena, not a discovery subpoena." Harbor Tech LLC v. Correa, 73 Misc.3s 1211(A), 2021 N.Y.Slip Op. 50995(U) (Kings Co. Civil Court Oct. 14, 2020, Stoller, J.).
creator
(1) For trusts, see settlor.
(2) NY EPTL 1-2.2 defines a creator as "a person who makes a disposition of property."
credit quality
For a bond: The "likelihood that the borrower will make the promised payments and return the principal." Penelope Wang, 8 Things You Need to Know About Bonds, AARP Bulletin, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link).
credit risk
The risk that a borrower will default on a loan.
Credit Suisse
Switzerland's second-largest bank by assets; based in Zurich. • Caitlin McCabe & Josh Mitchell, Why Is Credit Suisse in Trouble? The Banking Turmoil Explained, WSJ, March 16, 2023 (Apple News link):
Zurich-based Credit Suisse [pronounced Credit Swees] traces its history back to 1856, when it was founded to finance the expansion of Swiss railroads. Today, it stands as Switzerland’s second-largest bank by assets, trailing UBS Group.
The bank’s main business is managing money and creating investment products for wealthy clients around the world. . . .
credit washing
A type of bank fraud. • "Co-conspirators Rahne Cooper and Darius Hinton previously pled guilty to committing bank fraud for their illegal use of synthetic identities. // Russell agreed to plead guilty to participating in an extensive, multi-year conspiracy to obtain more than $2.5 million from at least 12 financial institutions and the United States Small Business Administration. According to the government, Russell used a synthetic identity because she had poor credit. Beginning in August 2017, Russell embarked on a new scheme, known as credit washing, to remove legitimate debt accounts from her credit history by falsely claiming she was the victim of identity theft and had not opened those accounts. Once the credit reporting agencies removed those accounts, her credit score improved, enabling her to obtain credit. She and her unnamed co-conspirators continued to make these false claims of identity theft, demanding the credit reporting agencies remove newly opened accounts. As a result, financial institutions relied on these washed credit reports in deciding whether to extend her credit." Attorney pleads guilty to fraud conspiracy and filing false tax return, IRS, Jan. 20, 2022.
CRE industry
The CRE industry, or commercial real estate industry, is a sector of the real estate market that involves the buying, selling, leasing, and management of commercial properties such as office buildings, retail spaces, warehouses, and industrial properties. The industry includes a wide range of professionals, including real estate brokers, developers, investors, property managers, appraisers, and attorneys. The CRE industry plays a significant role in the economy by facilitating business expansion, job creation, and tax revenue generation.
cryogenic freezing
"[T]he process of preserving bodies in the hope that modern science can resurrect them in the future . . . ." Hayley Cuccinello, How the rich use trusts to take care of pets and pay for cryogenic freezing, Business Insider, July 26, 2023 (Apple News link).
cryptocurrency
"[A] type of virtual currency that utilizes cryptography to secure transactions that are digitally recorded on a distributed ledger. See Rev. Rul .2019-24." Rev. Rul. 2023-14. • "[Paul Singer] says crypto is 'completely lacking in any value. It is not a substitute for gold, but it has taken away some of the demand side for gold.' He adds: 'There are thousands of cryptocurrencies. That's why they're worth zero. Anybody can make one. All they are is nothing with a marketing pitch--literally nothing.'" James Freeman, Paul Singer, the Man Who Saw the Economic Crisis Coming, WSJ, April 7, 2023 (Apple News link) ("He warned about subprime mortgages before 2008, Dodd-Frank in 2010, and inflation in 2020. After Silicon Valley Bank, what does he think is next?)". C.f. gold.
CUSIP number
A bond's alphanumeric identifier. • You can search using the CUSIP number on Trace, the Financial Industry Regulatory Agency's price-reporting system.
D
Danegeld
In feudal times, a direct tax levied throughout England.
dapps
See decentralized apps.
DAPT
An acronym that stands for domestic asset protection trust. • In some states, a DAPT can be structured so the grantor is a beneficiary. See self-settled trust.
dead hand
"[A] strategy that allows the owner of an estate to control beneficiaries and property even after death." Susan R. Lipp, Note From the Editor, Trusts & Estates Magazine, May 2024.
debate
A formal discussion of perspectives over which there is disagreement.
de facto
Existing in fact; having effect even though not legally recognized. C.f. de jure.
de jure
Existing according to law. C.f. de facto.
death benefit
The proceeds of a life insurance policy that are paid out tax-free to designated beneficiaries (or to the policy owner's estate).
Death on the High Seas Act (DOSHA)
"Under the 100-year-old law, damages are limited to the support a person killed would have provided to his or her survivors. Under Dohsa, the plaintiff must prove that either negligence or poor judgment of a vessel’s owner caused the death of their loved one, or that the vessel was not seaworthy." Joel Rosenblatt & Teresa Xie, Doomed Submersible's Waivers Aren't Enough To Ward Off Lawsuits, Financial Advisor, June 23, 2023.
death-put redemption clause in a certificate of deposit
A feature in a certificate of deposit that allows a decedent's estate to redeem the CD at face value in the event the holder of the CD dies before the CD's maturity date. • See Hani Sarji, What is a Death-Put Feature of a Certificate of Deposit?, Wills, Trusts, Estates, April 3, 2022.
death tax
(1) A term that applies either to an estate tax or an inheritance tax. • This use of the term is politically neutral.
(2) The pejorative label for the "estate tax" given by its opponents.
decanting
When statutory requirements are met, a way for a trustee to modify an otherwise irrevocable trust by transferring assets to a new trust. See NY EPTL 10-6.6. • Generally, decanting involves examining the language of an existing trust, creating a new trust with more desirable language, and moving the assets of the existing trust to the new trust.
decedent
An individual who has died.
decentralized apps
Software that allows users to access decentralized finance platforms. • Decentralized apps are popularly called "dapps."
decentralized finance
Paul Vigna, DeFi Is Helping to Fuel the Crypto Market Boom -- and Its Recent Volatility, WSJ, June 3, 2021 (Apple News link):
Short for decentralized finance, DeFi is an umbrella term for financial services offered on public blockchains. Like traditional banks, DeFi applications allow users to borrow, lend, earn interest, and trade assets and derivatives, among other things. The collection of services is often used by people seeking to borrow against their crypto holdings to place even larger bets.
There are two key differences from mainstream banks: All services are for digital currencies instead of government-issued ones such as the dollar and the euro, and there is no intermediary or centralized system through which transactions are processed.
. . .
DeFi is still an immature and highly risky market. In some cases, those running the apps are anonymous, making it harder for users to determine which platforms are reliable. The services aren't regulated or insured, so if a platform fails there is no recourse.
Another risk is security. . . .
declaratory judgment
A type of relief that declares the rights, duties, or legal status of the parties without ordering any action or awarding any damages.
decumulation
The phase in life when someone retires and must live off of their retirement savings without running out of money. • See Stephen Chen, Why Retirement Decumulation Is The New Accumulation, Forbes, Sept. 30, 2019 ("It’s much more complex than the accumulation of assets.").
deed
A document that conveys title to real property.
default rule
A rule that applies when a legal instrument is silent. Also called "off-the-rack rule" or "off-the-shelf rule." • See the 📖Glossary book for additional details.
defective grantor trust
See intentionally defective grantor trust.
defendant in error
See appellee.
DeFi
demesne
Part of a manor either kept by a lord in his own hands or farmed for his own profit.
dependent tenure
In medieval England, after the Norman conquest, the principle that except for the king, every person holds land under some lord. • See tenure.
deposit betas
"[T]he portion of rate changes that banks pass on to depositors." Jon Sindreu, Banks Can't Shortchange Savers Forever, WSJ, July 13, 2023 (Apple News link).
derivative claim
"A derivative suit is instituted by the owner of the business to prosecute a claim on behalf of the company. This frequently applies when those charged with availing the business of court rem- edies are the alleged wrongdoers. A derivative claim belongs to the business and not the owner . . . . To determine whether a cause of action is personal (to the trust) or derivative, “the pertinent inquiry...‘is whether the thrust of the plaintiff’s action is to vindicate his [or her] personal rights as an individual and not as a stockholder on behalf of the corporation.’” Bibbo v. Arvanitakis, 145 A.D.3d 657 [2d Dept 2016]. The ultimate question, therefore, is where does the recovery go?" Michael Calcagni & Michael J. Borger, Standing of Trust Beneficiaries in Derivative Actions, NYLJ, Sept. 10, 2023. • Derivative claims include (1) diminution in the value of shares, (2) waste and mismanagement by the board of directors, (3) damage to a corporation's reputation and associated goodwill due to chairman misconduct, and (4) diversion of corporate opportunities.
derivative suit
See derivative claim.
designated Roth contribution
A type of employee retirement contribution where a portion of an employee’s salary is withheld after-tax and transferred into an employer-sponsored retirement plan — 401(k), 403(b), or governmental 457(b) plans. • Unlike pre-tax elective contributions, designated Roth contributions are currently includible in gross income but tax-free when distributed. If a plan permits designated Roth contributions, it must also offer pre-tax elective deferral contributions. • C.f. elective deferral contribution.
devisable
The right to transfer property at death by a will.
devise
Traditionally, the transfer of any property at death by a written document called a "will." Today, the term is limited to transfers of real property by will. • NY SCPA § 103(12) defines the word devise when used as a noun as "a transfer of real property by will," and it defines devise when used as a verb (i.e., "to devise") as "to transfer real property by will." • Adding the word "devise" to a disposition can indicate that the testator intended to have title to real property pass to the beneficiaries instead of having the executor sell the property and distribute the proceeds: "It is observable that the language of the testator is very carefully employed to rebut the theory of [an equitable] conversion. In each of five articles, when giving income merely, he uses the phrase 'I give and bequeath,' appropriate to a mere gift of personal property, but when he creates the remainders, the language changes uniformly and in every instance and becomes 'I give, devise and bequeath.' The change of phraseology seems not to be accidental, but intentional, and to indicate the testator's expectation that land, as such, would pass in the remainders, and their gift require the added word 'devise.'" Scholle v. Scholle, 21 N.E. 84 (N.Y. Ct. Appeals 1889).
devisee
A person who receives real property under a will. • See NY EPTL 13-4.1(b); NY SCPA § 103(13). C.f. legatee.
dicta
“[S]tatements that are not part of the court’s holding. Common signs that statements are dicta include words or phrases such as if, for example, suppose, or other language indicating that statements are analogies, generalizations, hypotheses, illustrations, or mere passing observations. In such statements a judge may, for any number of reasons, expound on irrelevant or nonexistent facts or a theory of law that was not applied. Dicta have no authority, so don’t rely on them. But they may offer insight into how the court might rule given a different set of circumstances.” Bryan Garner, The Redbook: A Manual on Legal Style, 3d 371.
digital asset account
"A digital asset account or wallet generally provides its owner or custodian with the ability to store the public and private keys to digital asset holdings. These keys are required to conduct transactions with the digital assets associated with those keys and thus to control the ability to transfer those digital assets. . . . Some wallets may provide additional or different capabilities beyond storing keys. Wallets can be digital (software) or physical (hardware) and can be connected to the Internet (hot) or disconnected from the Internet (cold). Wallets can be custodial (hosted) or non-custodial (unhosted)." Gross Proceeds and Basis Reporting by Brokers and Determination of Amount Realized and Basis for Digital Asset Transactions, Proposed Rule by the IRS, Aug. 2023. See hosted wallet and unhosted wallet.
digital assets
"Digital assets are digital representations of value that use cryptography to secure transactions that are digitally recorded using distributed ledger technology on a distributed ledger, such as a blockchain or similar technology. Digital assets do not exist in physical form. Depending on the particular digital asset, individual units of a digital asset may be referred to as coins or tokens. Some digital assets are referred to as virtual currency or as cryptocurrency." Gross Proceeds and Basis Reporting by Brokers and Determination of Amount Realized and Basis for Digital Asset Transactions, Proposed Rule by the IRS, Aug. 2023.
directed verdict
A ruling made by a trial judge who concludes that there is no evidence for the jury to reach a different conclusion. • "A civil jury had heard about a week of testimony . . . .'No one is a bigger believer in juries than me,' [the judge] said. 'It was a difficult decision.' But he said the plaintiff had simply failed to prove his case and there was no need to send it to the jury." Scott Sandlin, Relative loses lawsuit against Abruzzos - Widower had filed financial claims, Albuquerque Journal, July 9, 2015.
directed trust
Allows non-trustees (such as advisors, committees, or protectors) to direct trustees regarding such matters as investments and distributions. • As of 2023, New York does not have a directed trust statute, but a statute was proposed. • "A directed trust may be a useful vehicle for digital assets, depending on the trust’s legal home state. A directed trust is a trust where someone other than the trustee is responsible for investment decisions. The laws regarding directed trusts vary among states. In some states the laws delineate the duties of an advisor versus those of a trustee. Additionally, some state laws obligate the trustee to oversee the advisor, thus leaving the trustee liable for losses. Other states define the advisor’s role as independent, theoretically shielding the trustee from liability." Wendy Hoey Sheinberg & Stella Lellos, Accounting for Digitgal Assets in Your Estate Plan, Rivkin Radler LLP, March 29, 2023.
disclaim
To reject a gift or a share in or payment of an estate. • New York uses the term "renunciation" instead of disclaimer. • A disclaimer is neither an assignment nor a release. In a disclaimer, the donee refuses something. In an assignment or release, the donee accepts something before transferring it.
discretionary fiduciary investment adviser
"[A] fiduciary role in which an adviser manages investments without calling the client for permission before each transaction." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023. C.f. [non-discretionary fiduciary investment adviser](#non-discretionary fiduciary investment adviser).
discretionary power of appointment
A power of appointment that permits the donee to exercise or not exercise it. NY EPTL 10-3.4(c).
discretionary trust
Trust in which income, as well as principal, is distributable to beneficiaries during the term of the trust not as a matter of right but solely in the discretion of the trustee.
disposition
NY EPTL 1-2.4 defines a disposition as "a transfer of property by a person during his lifetime or by will. Under this definition, property received from an intestate decedent is not received through a disposition because it is received neither through a lifetime transfer nor by will. Also, a court held that a surviving spouse's withdrawal from a bank account that was owned jointly with the decedent spouse is not an abatement of estate assets because it is not a disposition -- the transfer was made by the surviving spouse, not the decedent. Mason v Mason, 657 N.Y.S.2d 214 (App. Div. 3d Dep't 1997).
distributee
Someone who takes through the laws of intestacy. See EPTL 13-4.1(c); NY SCPA § 103(14).
Domesday Book
A survey of England that William the Conqueror ordered in 1086. It is England's earliest surviving public record. • "One explanation for the name of the book is that the records were deemed by the populace to be as conclusive as the day of judgment." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 31 n.13 (7th ed. 2020). • "The primary purpose of the survey was fiscal in nature. William desired precise, up-to-date information as to contributions made by each estate to the Danegeld, a direct tax levied throughout the country. Additionally, he sought an accurate and complete picture of the redistribution of English lands that had taken place in the 20 years since the Norman invasion." Id. at 6. • You can search the Domesday Book at https://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/domesday/
donor
(1) Respecting powers of appointment: "the person who creates or reserves a power." EPTL 10-2.2(a).
(2) Respecting trusts: See settlor.
Donor-Advised Fund (DAF)
A charitable giving account that allows the donor to recommend grants from the account to charitable organizations. • "You typically open a DAF with a community foundation or through the charitable arm of a brokerage firm, such as Vanguard or Schwab, and there's often no minimum deposit." Ryan Ermey, Warren Buffett shares details of his will—2 key lessons you can learn, 'whatever your wealth level', CNBC, Aug. 16, 2024 (Apple News link). • A DAF is useful for taxpayers with appreciated investments because it allows donors to deduct the fair market value of contributions of the appreciated assets to the DAF, and the taxpayer does not have pay capital gains tax on the appreciated assets.
double spacing
"Double spaced text has a blank line between successive lines of type. The space between lines is called leading and is measured in points from the bottom of one line of text to the bottom of the next. Double spaced text should have leading of at least the height of the type. Thus double spaced 14-point type must have at least 14 points of leading, for a total line spacing of 28 points. An attorney or litigant may rely on the line spacing setting of the word processing program used to create the brief." Supreme Court of the State of New York, Appellate Division: Second Judicial Department, A Glossary of Terms for Formatting Computer-Generated Briefs, with Examples.
double tapping
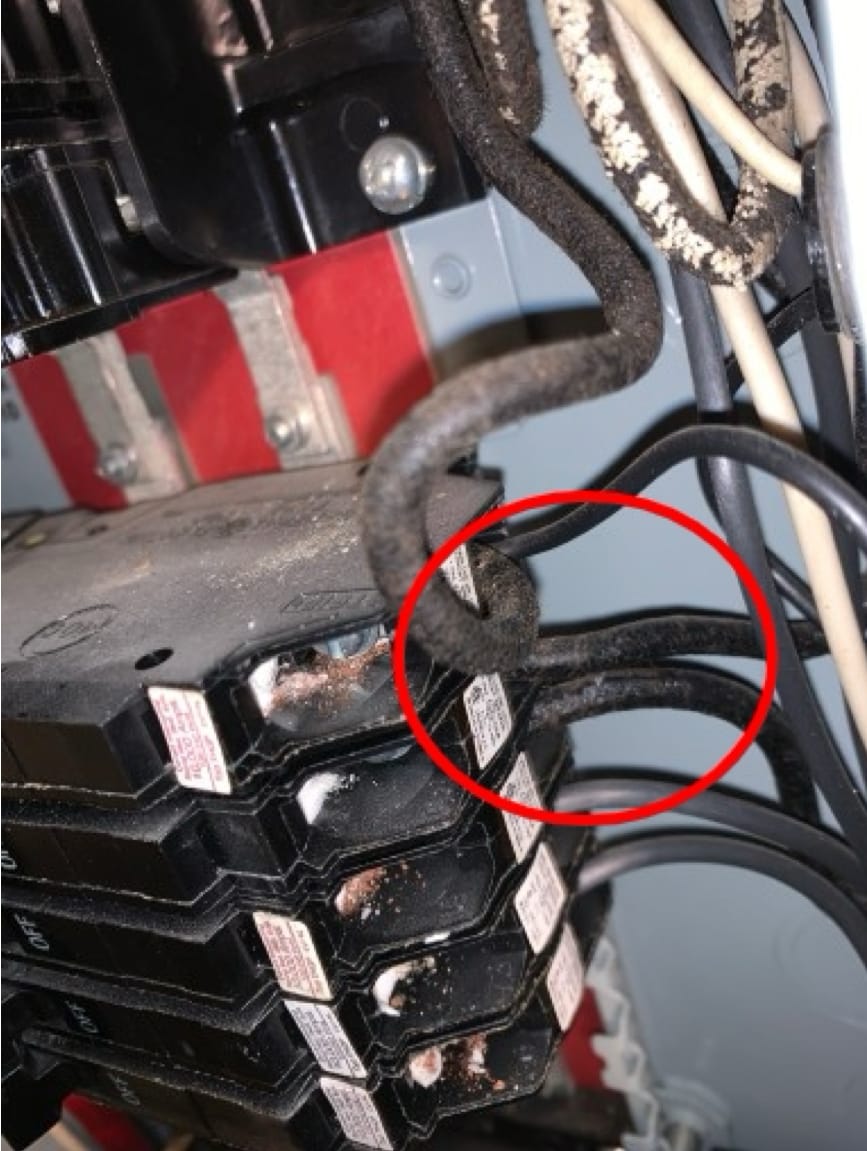
At an electrical panel: When two wires are connected to the same circuit breaker. Double tapping is not a good practice. It potentially causes overcurrent at the breaker and may overwhelm the electrical panel.

dovish
Monetary policy: Refers to an approach that is generally more supportive of lower interest rates and a looser monetary stance with the aim of stimulating economic growth. • Example: "Economists say a slower pace of runoff in the Fed’s bond portfolio could be dovish, as it takes a little pressure off long-term rates." Alice Uribe, Perpetual Sells Bonds, Cuts Cash as Fed Slows Pace of Quantitative Tightening, WSJ, June 20, 2024 (Apple News link). • C.f. hawkish.
draftsmanship
"[T]he art of expressing in a will the known desires of the testator." Jule E. Stocker, Jonathan J. Rikoon, Pamela R. Champine, & Janine Racanelli, Practising Law Institute: Stocker and Rikoon on Drawing Wills and Trusts (2011) (explaining, "We occasionally use less current terms for their nuances: 'draftsmanship' connotes more art than 'drafting' even though it includes a reference to the time when all drafters were draftsmen.").
due-on-sale clause
"[T]he term 'due-on-sale clause' means a contract provision which authorizes a lender, at its option, to declare due and payable sums secured by the lender’s security instrument if all or any part of the property, or an interest therein, securing the real property loan is sold or transferred without the lender’s prior written consent." 12 U.S.C. § 1701j-3(a)(1).
durable power of attorney
A power of attorney that remains in effect even when the principal becomes incapacitated. •
duress
In a will contest: "[S]omeone claims you only made the will because you were under extreme pressure by someone or something to divide your property in a way that goes against your wishes." Will Contests, New York City Bar Legal Referral Service.
duty of loyalty
In trusts: "The loyalty norm forbids the trustee from self-dealing with trust assets and from engaging in conflict-of-interest transactions adverse to the trust." John H. Langbein, The Contractarian Basis of the Law of Trusts, 105 Yale L.J. 625 (1995).
duty of impartiality
A trustee's duty to fairly balance the interests of two or more beneficiaries when investing, managing, and distributing the trust property. • The duty of impartiality arises when a trust has two or more beneficiaries, whether their interests are simultaneous or successive (i.e., income beneficiaries and remainder beneficiaries). Restatement (Second) of Trusts § 183 comment a (1959). • "The hallmark of the duty of impartiality is balance: The trustee must strike a fair balance between the beneficiaries, giving due regard to their respective interests." Jesse Dukeminier et. al., Wills, Trusts, and Estates 821 (7th ed. 2005).
duty of prudent administration
In trusts: "The duty of prudent administration is a reasonableness norm, comparable to the reasonable person rule of tort." John H. Langbein, The Contractarian Basis of the Law of Trusts, 105 Yale L.J. 625 (1995).
dwelling
NY MDL § 4(4)) defines a "dwelling" as "any building or structure or portion thereof which is occupied in whole or in part as the home, residence or sleeping place of one or more human beings." • See multiple dwelling.
dynasty trust
A trust that remains in place for multiple generations.
E
{id: echo-chamber-effect"
echo chamber effect
A situation where beliefs are amplified or reinforced by communication and repetition inside a closed system, often leading to a lack of exposure to differing viewpoints.
echo chambers
Environments where individuals are exposed predominantly to information and opinions that reinforce their existing beliefs.
economies of scale
Increasing the size of something, such as produced goods or 401(k) accounts, reduces the cost per item. • For Companies: Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that a company can achieve as it increases production levels. In simple terms, the more a company produces, the lower the cost per unit. This is because fixed costs, such as machinery and equipment, can be spread out over a larger number of units, resulting in lower average costs. Economies of scale are why larger companies often have a competitive advantage over smaller ones, as they can produce goods at a lower cost and sell them at a lower price while still making a profit. • For 401(k) Plans: "[L]arger plan sizes enable plan sponsors to negotiate better record-keeping fees, which can benefit both participants and the sponsor." Robert Powell, Your company may want to hold your 401(k) assets when you retire -- and you may want to let them, MarketWatch, Aug. 15, 2023 (Apple News link).
endowment fund
"When assets are contributed to a charity as 'endowment funds,' meaning that they are contributed subject to donor restrictions as to their expenditure, state law generally imposes specific restrictions on the charity's ability to invest and spend such assets." Antonia M. Grumbach, Charitable Asset Maintenance: Flexibility and Responsibility in the Not-for-Profit Arena (Oct. 2003).
education inflation
"For most of the past two decades, the cost of education rose more quickly than the general inflation rate, with the Consumer Price Index growing at 2.5% annually while the Tuition Index grew at 4%. Although this trend reversed in 2020 and has remained so since, it does not mean that education inflation has subsided. . . . Continually rising tuition costs underpin the importance for families to save early and frequently within a 529's tax-advantaged structure; the additional time helps harness the effects of compounding to keep up with these increasing costs." Hyunmin Kim, 529 Plans: What's Changed and What's the Same?, Morningstar, June 12, 2023 (Apple News link).
effective tax rate
"[A]n effective tax rate is the actual tax rate paid on total income. One way to calculate the effective tax rate is to add up the total amount of tax paid and divide that by taxable income. The quotient is the effective tax rate." TheStreet Staff, What Is a Marginal Tax Rate? Definition & Example, TheStreet, May 24, 2023 (Apple News link).
efficient market theory
"[I]dentified the difficulty of outperforming the market because information affecting price was quickly available and taken into account." Hon. C. Raymond Radigan, The Evolution of the Principal and Income Act Under the EPTL, NYLJ, May 19, 2004. • "Efficient market theory instructs us that it is impossible to outsmart the market by predicting which securities will do belter or worse. Owning many securities enhances the chances of offsetting losers with winners." John H. Langbein, The Uniform Prudent Investor Act and the Future of Trust Investing, 81 Iowa L. Rev. 641, 647 (1996).
ejector
Someone who dispossesses another.
elective deferral contribution
A type of employee retirement contribution where a portion of an employee’s salary is withheld pre-tax and transferred into an employer-sponsored retirement plan — 401(k), 403(b), or SIMPLE IRA plans. • The employee contribution is generally a percentage of the employee’s compensation, but some plans permit the employee to contribute a specific dollar amount each pay period. • Also called “salary reduction contribution.” C.f. designated Roth contribution.
eligible designated beneficiary
For years after 2020, with respect to inherited IRA accounts and retirement plans, a spouse or minor child of the deceased account holder, disabled or chronically ill individual, or an individual who is more than 10 years younger than the IRA owner or plan participant. An eligible designated beneficiary can take distributions over the longer of their own life expectancy and the employee's remaining life expectancy, or follow the 10-year rule (if the account owner died before that owner's required beginning date). Retirement Topics - Beneficiary, irs.gov.
emergency fund
Savings that someone uses only when certain events occur. • Money set aside for unforeseen expenses. • "There are no strict rules on what counts as an emergency, but as a general rule of thumb, it should only be used for essential expenses. . . . You should keep your emergency fund in a relatively accessible account . . . ." Alexandria White, Emergency funds can offset surprise medical bills, unemployment an more -- here's how to get started, CNBC, May 3, 2023. • See emergency fund articles on WTE.
enfeoff
In feudal times, to give land. • Responding to the 1166 questionnaire by Henry II asking about the number of knights enfeoffed on the tenant's land and the number required by his service, the return of the Archbishop of York wrote, "[O]ur predecessors enfeoffed more knights than they owed to the king, and they did this, not for the necessities of the royal service, but because they wished to provide for their relatives and servants.” Douglas and Greenaway, 2 English Historical Documents 907 (Oxford Univ.Press, 1953), quoted in Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 5 n.9 (7th ed. 2020).
"entity" approach to partnership taxation
An approach to taxing the income of a partnership that treats the partnership as an entity that is separate from its partners. C.f. "aggregate" approach to partnership taxation.
equitable adjustment
equitable apportionment
"Requiring a fiduciary to reallocate benefits or burdens is the doctrine of equitable apportionment. In after-death tax planning, the doctrine is called equitable adjustment." Joel C. Dobris, Limits on the Doctrine of Equitable Adjustment in Sophisticated Postmortem Tax Planning, 66 Iowa L. Rev. 273 (1981) (citations omitted). • See the 📖Glossary book for additional details.
equitable buyout
For an LLC: A court's equitable power "to order buyout damages under other circumstances not involving a member's decision to seek dissolution." Reliant Life Shares, LLC v. Cooper, 90 Cal. App. 5th 14 (CA Ct. Appeals, Second District, Division Eight, 2023). • "This is the [author's] first encounter with the concept of an equitable LLC buyout . . . . Under the holding of the Reliant LIfe Shares opinion, a trial court has authority to order an 'equitable buyout' of an LLC member as a remedy for the other members' wrongdoing." writes Kevin Brodehl in "Equitable Buyout" as a Remedy for LLC Wrongdoing?, JD Supra, June 26, 2023. C.f. statutory buyout. "As an equitable remedy, the application of equitable buyouts will be hyper-sensitive to the specific facts and claims of each case." • C.f. contractual buyout, statutory buyout.
equitable conversion
During the probate of a will, a transformation of real property to personalty by an executor that occurs when the executor sells the real property pursuant to a positive direction to convert the real property to personalty that is either expressed (i.e., there is an "explicit and imperative direction for its exercise") or implied (because it is necessary and essential for the disposition of the testator's estate to be carried out). Schoelle v. Schoelle, 21 N.E. 84 (N.Y. Ct. Appeals 1889). A discretionary power of sale does not result in equitable conversion. Id.
equity risk premium
"[E]ssentially the premium return that investing in stocks should provide versus a risk-free rate like the yield on U.S. Treasuries." Nicholas Jasinski, Saving the Banks Isn't Quantitative Easing, Barron's, March 20, 2023 (Apple News link).
escheat
The consequence of someone dying without an estate plan and without an heir: The decedent's estate goes to the government. • In medieval times, the decedent's estate would escheat to the overlord. Today, it escheats to the state where the property is located. • See Estate of Clark, 271 A.D. 691, 696, 68 N.Y.S.2d 487 (App. Div. 4th Dep't 1947) ("[T]itle vests in the State at once, upon the death of a decedent, intestate and without heirs or distributees.").
ESG factors
ESG is an acronym that stands for "environmental, social, and corporate governance." • "Environmental Social and Governance or “ESG” standards describe a broad array of criteria. Environmental factors examine environmental impacts (such as waste management and greenhouse gas production). Social factors focus on human rights violations and violations of labor laws (such as human trafficking and child labor in the supply chains), among other things. Governance factors consider longer-term value, positive and negative spillover effects, and whether a corporation has implemented structures and personnel with diverse perspectives to avoid the kinds of group-think that led to the mortgage crisis and Great Recession. Ultimately, ESG ratings allow investors, with an aversion to longer-term risks and with preferences beyond short term profit, to pick and choose where they invest their money." Tracey Roberts, Weekly SSRN Tax Article Review And Roundup: Roberts Reviews The Missing “T” in ESG By Chaim & Parchomovsky, TaxProf Blog, May 17, 2024. • See Tamara Keith, Biden has vetoed his first bill. Here's how that compares to other presidents, NPR, March 20, 2023 (Apple News link) ("the veto blocks a measure that was aimed at reversing a Biden administration rule for pension managers. The rule allows them to make investment decisions taking into consideration environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG) factors.").
estate
(1) All of the assets that someone owns. • An "estate" can have a different scope depending on the context, including probate estate, non-probate estate, gross estate for purposes of the federal estate tax. • NY EPTL 1-2.6(b) codifies this meaning of "estate": "The aggregate of property which a person owns."
(2) The interest a person has in property. • EPTL 1-2.6(a) codifies another meaning for "estate": "The interest which a person has in property."
(3) The estate of a decedent. • EPTL 11-1.1(a) ("Fiduciaries' powers") defines the term "estate" for purposes of EPTL 11-1.1 to mean "the estate of a decedent," "unless the context or subject matter otherwise requires."
estate planning
Planning for the accumulation, preservation, protection, decumulation, and transmission of wealth. • Estate planning is an umbrella term that encompasses different types of planning, including planning for incapacity, retirement, charitable gifting, paying for long-term care, the transmission of wealth in a family during life and upon death, and tax minimization. Estate planning is distinguishable from estate administration, a process which effectuates the plan. • A good estate plan must anticipate its successful administration. A comprehensive estate plan looks at "wealth" broadly to include not only an individual's assets, but also values. • Estate planning professionals include financial advisors, accountants, lawyers, and fiduciaries. • "Reframe your thoughts about estate planning. It is not only morbid thoughts of dying. Estate planning should be as much planning for life: retirement, illness, disability, young kids, college, etc. . . . Estate planning means retirement, insurance, and other planning." Martin Shenkman, New Year's Estate Planning Resolutions, Forbes, Dec. 28, 2022 (Apple News link).
estate tax
An estate tax is imposed on the estate of a decedent for the privilege of transferring property at death. • The IRS defines the estate tax as "a tax on your right to transfer property at your death." C.f. inheritance tax.
estate tax cliff
See tax cliff.
execute
To sign.
executor
Someone (an individual or corporation) named by a testator in a last will and testament to carry out the testator's directions. • Someone who manages a decedent's testamentary estate by probating the decedent's will, marshaling the decedent's assets, notifying creditors and persons interested in the estate's assets, paying outstanding debts, and distributing the decedent's remaining assets according to the terms of the will. • NY SCPA 103(20) defines "executor" as "[a]ny person to whom letters testamentary have been issued." • Powers of Sale in an Executor in Pennsylvania: "An executor is the person, or, in modern times, frequently a corporation, named to carry out the directions of a man's last will and testament. A testament relates solely to personal property, and a will to real estate, and the latter operates as a devise of the legal title and needs no executor. The office of an executor, therefore, pertains properly to the administration of the personal estate, and the executor has no authority over the real estate, except under a special provision to that effect contained in the will, or by virtue of an Act of Assembly." • For example, Oklahoma changes the default rule regarding wills and makes the personal representative necessary for the transfer of both a devise and a legacy: "In a specific devise or legacy, the title passes by the will, but possession can only be obtained from the personal representative; and he may be authorized by the district court to sell the property devised or bequeathed, in the cases herein provided." Ok. Stat. tit.84 Sec. 7 Title and possession - Representative may sell property devised (Oklahoma Statutes, 2023). • See fiduciary.
diversification
"Owning many securities enhances the chances of offsetting losers with winners." John H. Langbein, The Uniform Prudent Investor Act and the Future of Trust Investing, 81 Iowa L. Rev. 641, 647 (1996). • Diversification minimizes risk.
ex-dividend date
The ex-dividend date is the date on which a stock begins trading without the upcoming dividend payment. If you buy a stock on or after the ex-dividend date, you are not entitled to receive the dividend for that period. For example, if a company declares a dividend with a record date of May 1 and an ex-dividend date of April 28, anyone who buys shares on or after April 28 will not receive the dividend payment.
ex-dividend effect
The ex-dividend effect refers to the impact that the payment of a dividend has on the price of a stock. When a company declares a dividend, it sets a record date, which is the date on which shareholders must be on the company's books in order to receive the dividend. The ex-dividend date is typically set two business days before the record date. If an investor buys a stock on or after the ex-dividend date, they are not entitled to receive the upcoming dividend payment. As a result, the stock price may drop by the amount of the dividend on the ex-dividend date, as investors who are seeking to receive the dividend sell their shares to those who are not. This is known as the ex-dividend effect.
F
fair market value
"[T]he price at which the property would change hands between a willing buyer and a willing seller, neither being under any compulsion to buy or sell and both having reasonable knowledge of relevant facts." Reg. § 20.2031-1(b).
family office
"Family offices are privately owned entities established by affluent families to manage their wealth, plan for their families' financial future, engage in investment opportunities and provide other services to family members. Family offices can be formally structured or operated informally." Family Office, Day Pitney LLP. • "[M]ultifamily offices are typically only available to families with significant balance sheets—usually $10 million or more." Thomas J. Frank Jr., Family, Friends Aren't Always the Best Successor Trustees. Here Are 3 Alternatives., Barron's, Oct. 16, 2023 (Apple News link).
Fat FIRE
When someone has saved at least 25 time times their annual expenses (which is the traditional benchmark for financial independence, and spends more than the average American, which is about $61,000 per year, according to Census data. See Tanza Loudenback, What is Fat FIRE vs. Lean FIRE? 2 different ways to retire early, Business Insider, Nov. 12, 2020 (Apple News link). • "The [FIRE] movement even has offshoots, with some focusing on extreme frugality and others on building a large retirement fund or keeping a part-time job. . . . Those who like to spend more -- above six figures -- are part of Fat FIRE." Laila Maidan & Kathleen Elkins, FIRE Movement: Early retirees discuss limitation, need to resume working, Business Insider, Sept. 13, 2023 (Apple News link). • See financial independence and FIRE movement; c.f. Barista FIRE and Lean FIRE.
FDIC-insured sweep program
"FDIC-insured sweep programs are offered by brokerage firms. These programs 'sweep' client cash into FDIC-insured bank accounts. In some cases, clients’ deposits are fanned out across multiple banks to provide higher levels of FDIC protection. Like bank accounts, yield can vary across programs, with some programs offering highly competitive yields." Adam Grealish, Five Places to Put Cash Rather Than in the Bank, Kiplinger, May 1, 2023 (Apple News link).
fealty
In feudalism, a vassal's sworn loyalty and allegiance to a lord. • Fealty was an incident of tenure.
fear index
See volatility index.
fee
In feudal times land granted in return for military service. Also called a "fief."
fee-only advisers
Advisers who "have limited their role strictly to that of fiduciary by virtue of compensation that forgoes commissions for selling financial products." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
feudalism
The social structure of medieval Europe. It was pyramidal with the king at the top and peasants who tilled the soil at the bottom; everyone in between was both a lord over someone and a tenant under someone. The basis of rights and duties was typically status, not contract.
fiduciary
"The term 'fiduciary' means 'any person who occupies a position of peculiar confidence towards another.'" Sarah Patel Pacheco, Fiduciary Litigation: Avoiding (or Minimizing) the Traps, Tribulations, and Trials, 5 Est. Plan. & Cmty. Prop. L.J. 95 (2012), citing Montague v. Brassell, 443 S.W.2d 703, 713 (Tex. Civ. App.-Beaumont 1969, writ ref'd n.r.e.) (quoting Cartwright v. Minton, 318 S.W.3d 449, 453 (Tex. Civ. App.-Eastland 1958, writ ref'd n.r.e.). See executor, trustee. • See the 📖Glossary book for additional details.
fiduciary accounting
For a trust: Fiduciary accounting is the process of reporting and distributing the income and principal of the trust to the beneficiaries according to the terms of the trust document. Fiduciary accounting follows the rules and principles of the Uniform Principal and Income Act (UPIA) or the local trust law that governs the trust. Fiduciary accounting is mainly concerned with fulfilling the fiduciary duties of the trustee and ensuring that the trust assets are properly managed and distributed according to the trust document. C.f. tax accounting.
fiduciary duty
Duties that the law places on fiduciaries to compel them to act in the best interests of beneficiaries. • "[T]he beneficiary, not the trustee, bears the risk and receives the rewards of the trustee's bad or good management. If the trust property is invested wisely and produces handsome returns, the beneficiary, not the trustee, reaps most of the gains. If the trust property is invested poorly or is stolen by the trustee or others, the beneficiary, not the trustee, suffers the immediate consequences of the depletion in the trust fund. Putting aside reputational concerns and feelings of moral obligation (which is not to say that these considerations are unimportant), the problem is that trustee lacks a direct financial incentive to act with loyalty and care in managing the trust fund. The primary doctrinal answer to this problem . . . is the fiduciary obligation. The fiduciary obligation in trust law comprises duties of loyalty, prudence, and a host of subsidiary rules that reinforce the dudes of loyalty and prudence." Jesse Dukeminier et. al., Wills, Trusts, and Estates 771 (7th ed. 2005). • "Empowering the trustee to transact freely in the financial markets has shifted the locus of protection for beneficiaries from powers law to fiduciary law. Whereas disempowerment [under old rules] prevented the trustee from acting, modern trustees' powers law confers vast managerial discretion. Discretion entails the risk of harm as well as the opportunity to enhance the trust assets. To safeguard beneficiaries against abuse of this discretion, trust fiduciary law has developed as the functional replacement for the former scheme of trustee disability. Fiduciary law imposes two broad standards, loyalty and care, that regulate the exercise of the discretion that modern trustees' powers law bestows. . . . Trust fiduciary law regulates the trustee's exercise of discretion. Be it in trust law or in other fields of fiduciary obligation (for example, corporations, agency, or partnership), fiduciary duties are default norms imposed in juridical relations that feature 'scope for the exercise of discretion.' Fiduciary duties mean to 'induce the fiduciary to use his power beneficently.'" John H. Langbein, The Contractarian Basis of the Law of Trusts, 105 Yale L.J. 625 (1995).
fieri facias
Writ of execution directing a marshal or sheriff to seize and sell a debtor's property to satisfy a money judgment. • For example, Sands v. Codwise, 5 Johns. 536 (NY Court for Correction of Errors 1808), states (emphasis added), "When he stopped payment . . . judgment was entered up against him . . . . A fieri facias was soon after issued on the said judgment, which was levied on the household furniture, and other personal property of Comfort Sands, and on his dwelling-house in Pine Street, and another dwelling-house in Cedar Street. In November, 1798, the sheriff sold the personal property taken on the execution, at public auction, to the appellant . . . ."
filter buble
A state of intellectual isolation resulting from personalized searches and algorithmic curation, where users are exposed primarily to information that aligns with their existing beliefs.
final
Last; not necessarily free from error. • "There is no doubt that if there were a super-Supreme Court, a substantial proportion of our reversals of state courts would also be reversed. We are not final because we are infallible, but we are infallible only because we are final." Brown v. Allen, 344 U.S. 443, 540 (1953) (Jackson, J., concurring).
final expense insurance
See burial insurance.
final judgment
A final decision or order of a court that resolves a dispute and determines the obligations of the parties. C.f. order.
financial adviser
"[A] broad title that applies to several occupations that provide financial advising either by offering help with retirement, investments and budgeting or managing finances including taxes, estate planning, debt management and more. Financial advisers create and implement strategies to manage and balance portfolios." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
financial coach
Someone who teaches clients about financial planning but who does not give specific investment advice.
financial consultant
"[A] general term that can by used by anyone . . . who does financial planning, investment managment or financial coaching . . . ." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
{financial-elder-abuse}
financial elder abuse
"Any situation where a senior person is being financially victimized can be classified as financial elder abuse, said Jaime Levine, executive director of Elder Law and Advocacy, a San Diego nonprofit law firm." Carolyn Said, What Dianne Feinstein's Family feud can teach about the warning signs of elder financial abuse, San Francisco Chronicle, Aug. 17, 2023 (Apple News link).
financial independence
Having at least 25 times annual expenses saved. See Tanza Loudenback, What is Fat FIRE vs. Lean FIRE? 2 different ways to retire early, Business Insider, Nov. 12, 2020 (Apple News link).
financial planning
"[A]ny type of strategizing around the financial aspects of your financial life. These areas range from the basics such as budgeting to more complex areas such as saving and investing for retirement as well as estate planning for the distribution of your assets. In short, if it involves finances, then there’s a way to plan for it and optimize the outcome." James Royal, What is financial planning? Learn how to get started, Bankrate, June 27, 2023 (reviewing financial planning issues: budgeting, debt reduction, retirement planning, wealth management, tax planning, insurance planning, and estate planning).
FIRE movement
"FIRE" stands for "financial independence/retire early." "The formula is simple: A person needs to save up and invest 25 times their annual spending in order to become financially independence, assuming they plan to withdraw 4% of their nest egg each year thereafter." Tanza Loudenback, What is Fat FIRE vs. Lean FIRE? 2 different ways to retire early, Business Insider, Nov. 12, 2020 (Apple News link). "At that point, they no longer need to rely on a regular paycheck, to afford their lifestyle and they have the freedom to retire early." • "The FIRE movement's origins can be traced tot he 1992 book 'Your Money or Your life,' coauthored by a duo who had themselves achieved financial independence before their forties, and which is considered a bible for how to do the same." Laila Maidan & Kathleen Elkins, FIRE Movement: Early retirees discuss limitation, need to resume working, Business Insider, Sept. 13, 2023 (Apple News link). • There are three main categories of FIRE: traditional FIRE (which is defined here), Lean FIRE, and Fat FIRE; but there are now additional categories, including Coast FIRE. Id. • See financial independence.
firm risk
Risk "factors that touch the fortunes only of the individual firm." John H. Langbein, The Uniform Prudent Investor Act and the Future of Trust Investing, 81 Iowa L. Rev. 641, 647 (1996). C.f. industry risk and market risk.
first in, first out (FIFO) method
"[S]ecurities purchased earlier that likely have the most capital gains are sold. Normally, this would result in higher capital gains, but . . . that in a year where you have no additional income, selling assets with the highest profits could be advantageous. If your brokerage account allows you to sell by lots, you can select which shares to sell based on the capital gains they have accumulated . . . ." Laila Maidan, How to pay 0% capital gains tax on up to $123,250 of income, Business Insider, June 22, 2024 (Apple News link). C.f. last-in, first-out (LIFO) method.
flat tax
A tax that imposes the same tax rate on all taxpayers, regardless of whether the taxpayers are lower-income or higher-income. C.f. progressive tax, regressive tax.
flood zones
"Flood zones are land areas identified by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) on Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs). Each flood zone describes a land area in terms of its risk of flooding. FEMA’s FIRMs are created through an extensive mapping process and take into account many factors, including the types and strength of storms that historically have affected the area and the onshore and offshore topography. . . . FEMA flood zones are used to determine flood insurance rates as well as flood resistant construction requirements." Climate Resiliency Initiatives - Frequently Asked Questions, NYC Department of City Planning.
font
See typeface.
Form 941
A federal income tax form for employers that pay employees and withhold federal and FICA (social security and Medicare) taxation. See About Form 941, Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, IRS.
four unities test
For a joint tenancy, as described by Blackstone: "the unity of interest, the unity of title, the unity of time and the unity of possession; or in other words, joint tenants have one and the same interest, accruing by one and the same conveyance, commencing at one and the same time, and held by one and the same possession." 2 Bl.Comm. 180, qtd in Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 290 (7th ed. 2020) (explaining, "The requirement of unity of possession does not mean actual possession. There may be a joint tenancy in a future interest, such as a remainder. A unity of right to possession is sufficient.").
frankalmoin tenure
In feudalism, a tenure that arose from a gift of lands to a church or religious official (not a lay person), in return for religious (not secular) services, such as saying prayers. •"Frankalmoin" means "free alms."
free tenure
In feudalism, tenure where the services were definite and certain and were worthy of a free man; the services were not dependent on the lord as to amount or quantity. • Free tenure had four main divisions: (1) Tenure by knight service, (2) serjeanty, (3) frankalmoin, and (4) free and common socage. • Free tenants were protected by the king's courts (not just the lord's court) and had the benefit of real actions. • C.f. unfree tenure.
freeman
In feudal times a man who was free and might hold land but who owed some services to his lord. C.f. slave.
funeral insurance
See burial insurance.
future interest
An estate in land to which the holder is or may be entitled to possession in the future. • The federal gift tax regulations define a future interest as any interest in property “limited to commence in use, possession, or enjoyment at some future date or time.” Reg. § 25.2503–3(a). • C.f. present interest. See reversion.
G
gaslighting
"[T]he act of when someone is talking to or communicating with you, making you feel like your reality is being questioned." Angela Haupt, 7 Things to Say When Someone Gaslights You, Time, June 26, 2024 (Apple News link). • Haupt gives an example of gaslighting: "[Y]our boss gives you an assignment but omits crucial information, later berating you for falling short and claiming you were provided with the exact instructions you know you never received."
gavelkind tenure
In feudal times, a tenure that prevailed in the county of Kent and had special rules, including that on the death of an owner, land descended to all of his sons equally. C.f. burgage tenure, primogeniture.
general denial
A pointed and total denial of everything in a complaint or a paragraph of a complaint. • Example of a general denial in an answer: "Defendant denies all the allegations of the complaint." • In New York, it is "[i]mproper for [a] lawyer to interpose general denial knowing that his client has no valid defense." [Opinion #469 - 6/7/77 (64-77)](https://www.nysba.org/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id: 7641), New York State Bar Association.
general power of appointment
The power to vest a trust's principal in oneself.
generation-skipping transfer
Generally, a transfer that skips the estate tax for a generation.
generation-skipping transfer tax (GSTT)
A tax on wealth transfers that skip one or more generations. • The GSTT was originally enacted in 1976. But in the Tax Reform Act of 1986, the Reagan administration repealed the 1976 version, and enacted a new version, effective October 23, 1986.
gift tax
"The gift tax is not a property tax. It is a tax imposed upon the transfer of property by individuals. It is not applicable to transfers by corporations or persons other than individuals." Reg. 25.0-1 (b).
gig work
An activity that earns income through a digital platform (an app or website), including driving a car for booked rides or deliveries; renting out property or part of it; running errands or completing tasks; selling goods online, renting equipment; providing creative or professional services; and providing temporary, on-demand, or freelance work. See Manage Taxes for Your Gig Work, irs.gov; The Gig Issue, Millie, Fall 2022 (Apple News link).
gold
According to Paul Singer: "'. . . it is the only 'real' money and has occupied that status for literally thousands of years.'" James Freeman, Paul Singer, the Man Who Saw the Economic Crisis Coming, WSJ, April 7, 2023 (Apple News link). C.f. cryptocurrency.
gold IRA
A retirement account that holds physical precious metals, including gold, silver, platinum, and palladium; rather than stocks, bonds, and other paper assets. • "Many investors turn to gold IRAs to diversify their portfolios and potentially protect against inflation." Tim Maxwell, What is a gold IRA?, CBS News, March 20, 2023 (Apple News link).
governance
Rules, laws, or procedures that groups or entities adopt to provide a structure for communication, decision-making, accountability, and conflict resolution.
government bond
A bond that is issued by the U.S. treasury or entities affiliated with the federal government.
Grammarly
A tool that utilizes the power of artificial intelligence to enhance your writing. It works by analyzing your text and providing suggestions on how to improve grammar, spelling, punctuation, and style. With Grammarly, you can write with more confidence, knowing that your text is error-free and easy to read. See https://www.grammarly.com/
grand serjeanty
In feudal times, a type of serjeanty tenure held directly of the king and requiring an honorary ceremonial service. • "[W]ardship was incident to grand serjeanty, but not to petit serjeanty . . . ." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 31 n.24 (7th ed. 2020).
grantor
(1) For trusts, see settlor.
(2) For deeds, the person conveying title.
grantor trust
A trust in which the grantor of the trust is treated as the "owner" of all or part of the trust for income tax purposes, and all taxes are passed through to the grantor as if the trust did not exist. C.f. non-grantor trust.
gray divorce
A term used to describe the phenomenon of couples who divorce later in life, typically after the age of 50. • This type of divorce can be more complicated than divorces earlier in life. Gray divorce can have a significant financial and emotional impact on both parties, as they may not have the same earning potential or ability to start over as they did when they were younger. Catherine E. Shoichet & Parker Leipzig, More Baby Boomers are Living Alone. One Reason Why: 'Gray Divorce', CNN, Aug. 5, 2023 (Wealth Advisor link).
gross estate
"A gross estate encompasses all assets owned by an individual at the time of death." Gross Estate vs. Probate Estate, Smart Asset, July 28, 2023. C.f. probate estate.
gross negligence
Wanton or reckless conduct affecting the life of another.
gross pay
The total amount of money an employee earns before any payroll deductions are subtracted. C.f. net pay.
guardian ad litem (GAL)
A court-appointed adult that represents a minor child or legally incompetent person. The GAL is only a guardian for a specific lawsuit. • Also known as "special guardian." • Example: "The special guardian has filed two objections to the executors' account. . . . The special guardian represents infant contingent remaindermen of the residuary trust and of another trust set up in clause Twelfth . . . ." Estate of Warms, 140 N.Y.S.2d 169 (Sur. Ct. 1955).
guardian by nature
"At the common law, where there was no guardian in socage, the father was guardian by nature to his heir apparent, until he arrived to the age of 21; this guardianship gave a control of the person only, and not of the estate, real or personal, of the infant. . . . A guardian by nature has no control over the real or personal estate of his infant children." Combs v. Jackson, 2 Wend. 153 (N.Y. 1828).
H
{id habendum-clause}
habendum clause
In a deed, a clause that describes the estate granted. It starts with the words, "to have and to hold." • For example, a habendum clause for a fee simple title states, "to have and to hold the premises herein granted unto the party of the second part, the heirs or successors and assigns of the party of the second part forever."
hawkish
Monetary policy: Describes a policy stance that favors higher interest rates to combat inflation. C.f. dovish.
health care proxy
A legal document that gives someone (known as the health care agent) the legal authority to make medical decisions on the principal's behalf after a severe injury or illness.
heir
A person who is entitled to inherit under the default intestacy statutes in the absence of an estate plan. Heirs are determined when someone dies. "Typically, heirs are limited to persons who are descendants, ancestors, or collaterals of the intestate, but intestate's spouse, who is typically not an heir, may be entitled to some portion of the intestate's estate." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 31 n.37 (7th ed. 2020). • At common law, heirs inherited real property. See Jones v. Kelly, 13 N.E. 443 (N.Y. Ct. Appeals 1902). • See the definitions of collateral heirs, escheat, "laughing" heir, lineal ancestors, and lineal descendants. C.f. next of kin.
high-net-worth individuals (HNWI)
"[A]nyone with investible assets of $1 million and above, excluding their primary residence . . . ." They include "millionaires next door", midtier millionaires, and ultra-high-net-worth individuals. Quentin Fottrell, 'We've never seen this before': Millionaires are doing something unusal to preserve their wealth -- and you can do the same, MarketWatch, June 28, 2023 (Apple News link). • "Edward Jones Generations will include financial planning and investment management, focusing on clients with at least $10 million in investable assets. Representatives from Ernst & Young and the law firm Husch Blackwell will help Edward Jones’ financial advisors with tax and legal issues." Patrick Donachie, Edward Jones Launches New Model Focused on HNW Clients, WealthManagment.com, March 12, 2025.
high-yield bonds
See junk bonds.
holographic will
A will that is handwritten. See, e.g., North Dakota Supreme Court: Holographic Will Not Valid When Material Portions Not Proven To Be In Decedent’s Handwriting, Probate Stars, Jan. 11, 2022.
homage
In medieval times, a ceremony in which a vassal knelt before a lord, acknowledged himself to be his lord's man, and swore allegiance to the lord. Frequently, the lord made a grant of land to the vassal or gave the vassal an annuity. • Homage was an incident to tenure by knight service, but it became obsolete when knight service changed from actual military service to a monetary obligation. See fealty, feudalism.
honour
In medieval times, a larger baronial estate of a lord, which was comprised of numerous smaller estates that were held by different people. • "As many as 80 English estates, situated in different regions, were combined to compose a single lord’s honour. In the course of the Norman settlement, several thousand smaller estates were compressed into fewer than 200 major honours. The lords of these honours were the men who, with William, established the new English state." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, [Introduction to the Law of Real Property 2 (7th ed. 2020) (affiliate link)](https://www.amazon.com/Introduction-Historical-Background-Application-Hornbooks-ebook-dp-B084Q17HSQ/dp/B084Q17HSQ?_encoding=UTF8&me=&qid: 1650114347&linkCode=ll1&tag=wteinfo-20&linkid: 1dcb02bc9a77096c0a8a8dac4bd504df&language=en_US&ref_=as_li_ss_tl). • See Norman Conquest.
hosted wallet
"Some owners [of digital assets] use the services of a hosted wallet provider that stores their public and private keys. A hosted wallet provider may also maintain balance information, provide cybersecurity services, and facilitate the owners’ ability to own, and conduct transactions using, digital assets. These services may also include providing owners with online platforms that directly link owners to third party services that allow owners to buy and sell digital assets held in their hosted wallets." Gross Proceeds and Basis Reporting by Brokers and Determination of Amount Realized and Basis for Digital Asset Transactions, Proposed Rule by the IRS, Aug. 2023. See digital asset account and digital assets. C.f. unhosted wallet.
human composting
Having one's body turned into soil after death. • In 2019, Washington was the first state to legalize human composting. Other states that allow it are California, Colorado, Oregon, New York, and Vermont. See James FitzGerald, New York approves composting of human bodies, BBC News (Apple News link).
hybrid DAPT
A self-settled domestic asset protection trust where the grantor is not one of the initial beneficiaries, but the trust has someone acting in a non-fiduciary capacity who is given a limited right to add new beneficiaries--one of which is the trust's settlor. See DAPT, self-settled trust.
I
"I love you" will
A last will and testament in which the testator bequeaths to the surviving spouse everything that the testator owns and can pass by probate. • An "I love you" will might be simple, but it has downsides. See Hani Sarji, "I Love You" Will Might Not Show Love to Surviving Spouse, Wills, Trusts, Estates, Feb. 12, 2022.
ICE U.S. Dollar Index
Launched in 1985, this index "measures the currency [i.e., the dollar] against a basket of its biggest trading partners . . . ." Chelsey Dulaney, Megumi Fujikawa & Rebecca Feng, Dollar's Rise Spells Trouble for Global Economies, WSJ, Sept. 18, 2022 (Apple News link).
Illinois Senior Citizens Real Estate Tax Deferral Program
What is the Senior Citizens Real Estate Tax Deferral Program?, Illinois Revenue:
The Senior Citizens Real Estate Tax Deferral Program provides tax relief for qualified senior citizens by allowing them to defer all or part of their property tax and special assessment payments on their principal residence. The deferral is similar to a loan against the property's fair market value. Deferred amounts are borrowed from the state, who then pays the tax bill to the County Collector's Office. Interest on the amount paid by the State accumulates and a lien is placed on the property for all deferred tax payments and interest. (320 ILCS 30/1 et. seq.).
illiquid estate
A decedent's estate that does not have sufficient cash to pay taxes (estate, death, or inheritance taxes) or credit claims before making distributions to beneficiaries or heirs.
ILIT
An acronym for irrevocable life insurance trust.
impounded document
Respecting New York WebSurrogate: A document that is not listed on WebSurrogate. • See WebSurrogate December 2021 Upgrade Info, nycourts.gov; Hani Sarji, New York County Surrogate's Court Records Will Be Available on WebSurrogate Starting 11/6/2023, Wills, Trusts, Estates, Nov. 3, 2023.
incidents of tenure
In feudal times, implied rights granted to a lord and implied obligations imposed on a tenant that were additional to the particular services required of a tenant to the lord. These rights arose from the feudal relationship, not from any express agreement by the tenant. • See tenure.
income-driven repayment (IRD) plan
A plan that allows student-borrowers to repay their student loans as a percentage of income, instead of a standard monthly payment that is based on the amount borrowed and the interest rate.
Incomplete Non-Grantor Trust (ING)
A trust whose funding is an incomplete gift for purposes of the gift tax but a complete transfer for the purposes of the income tax. The trust must be formed in a state that allows domestic asset protection trusts and has a fiduciary state income tax. • "The primary use for an ING Trust is to save state income taxes. Therefore, the typical client is a resident of a state with a high state income tax who is either selling a business or other asset that will have a large capital gain or who has an asset, such as a large brokerage portfolio, that has sizable distributions that would be taxed by the client’s home state if the client hadn’t set up the ING Trust. It is important to note that income earned by an asset, such as a locally-run business or local real estate, is considered sourced to the client’s home state and therefore cannot avoid state income taxes using the ING Trust." Steven J. Oshins, Why Do Nevada and Delaware Get Most of the ING Trust Business?, Ultimate Estate Planner, July 1, 2023. • The grantor cannot be a trustee of an ING, and the trust must have a Distribution Committee.
index number
A unique identification number assigned to each case by the court.
indictment
"[A] formal charge outlining allegations against the defendant--all defendants are presumed innocent until proven guilty in a court of law." Kelly Phillips Erb, Two Promoters Charged In Alleged Trust Tax Shelter Fraud Scheme, Forbes, Sept. 26, 2023 (Apple News link).
individual retirement account (IRA)
"[A] personal account set up at a brokerage firm or mutual fund company that the saver manages." Adam Shell, Rolling Over a 401(k) Into an IRA, Kiplinger, July 16, 2024 (Apple News link).
Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN)
"[A] tax processing number issued by the Internal Revenue Service. The IRS issues ITINs to individuals who are required to have a U.S. taxpayer identification number but who do not have, and are not eligible) to obtain, a Social Security number (SSN) from the Social Security Administration (SSA)." Individual Taxpayer Identification Number, IRS.gov.
individually managed account
See separately managed account.
industry risk
Risk that "is specific to the firms in a particular industry or an industry grouping." Langbein, The Uniform Prudent Investor Act and the Future of Trust Investing, 81 Iowa L. Rev. 641, 647 (1996). C.f. firm risk and market risk.
inflation
Prices rise; the value of money decreases. • "Inflation is a measure of how quickly prices are rising over a given period of time. . . . [I]t's a useful way of measuring how our spending power has changed over time." Ruth Emery, What is inflation and how does it affect you?, Money Week, Nov. 15, 2022 (Apple News link).
inflation rate
"[T]he rate of change in prices." James Broughel, Why Raising Taxes Is A Misguided Approach To Inflation Control, Forbes, March 24, 2023 (Apple News link).
informal settlement of an estate
See non-judicial settlement of an estate.
inheritable
Property that, upon an individual’s death and in the absence of a will, passes to legally recognized heirs under the laws of intestacy. Inheritable property typically includes assets that are solely owned by the decedent and do not have designated beneficiaries or joint ownership arrangements that transfer ownership automatically at death. Intestacy statutes govern how such property is distributed, often prioritizing close relatives such as spouses, children, and other family members in a legally defined order.
inheritance
Property or assets received from a deceased individual, either through a will (probate property), by operation of law (non-probate property), or under the laws of intestacy if there is no will. Inheritance includes all property passed down to heirs or beneficiaries, whether by will, trust, joint ownership with rights of survivorship, direct beneficiary designations, or, in the absence of a will, through the statutory rules of intestate succession.
inheritance tax
An inheritance tax is imposed on each beneficiary of an estate for the privilege of receiving property from the dead. C.f. estate tax.
installment debt
Closed-ended loans. "They work by providing a lump sum, which you then repay the lender in regular payments that are typically the same amount each month and for a set time." Investopedia, Debt: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link). C.f. revolving debt.
installment loan
See installment debt.
insurable title
Title that an insurance company will be willing to ensure, even though there might be a defect (such as an ancient mortgage). C.f. marketable title.
intentionalist
"[I]ntentionalists prioritize (at least when compared to textualists) the intentions of the enacting legislature. See, e.g., Caleb Nelson, What Is Textualism?, 91 Va. L. Rev. 347, 351-52 (2005) ('[I]ntentionalists call upon courts to try to enforce the directives that members of the enacting legislature understood themselves to be adopting.')." Gregory A. Elinson & Robert H. Sitkoff, When a Statute Comes with a User Manual: Reconciling Textualism and Uniform Acts, 71 Emory L.J. 1073 (2022). C.f purposivist.
intentionally defective grantor trust (IDGT)
A trust that is treated as owned by its creator for income-tax purposes and by the beneficiaries for wealth-transfer tax purposes. See grantor trust, [non-grantor trust](#non-grantor trust).
inter alia
Among other things.
interest rate risk
"If interest rates rise, the value of long-term bonds will suffer a far greater decline in price than bonds with shorter-term maturities." Paul S. Lee, Implementing Total Return Trusts (2002).
Internal Revenue Code (IRC)
The federal tax statutes in the United States. • "Tax statutes had different iterations before they were officially codified in 1874. The tax code was formally titled the Internal Revenue Code in 1939, and Congress made revisions in 1954 and 1986." TheStreet Staff, What Is the Internal Revenue Code? Definition & History, TheStreet, Jan. 31, 2023 (Apple News link).
Internet Tax Freedom Act (ITFA)
Christine Kim, Weekly SSRN Article Review And Roundup: Kim Reviews The Internet Tax Freedom Act At 25 By Hellerstein & Appleby, TaxProf Blog, April 28, 2023:
The ITFA was enacted in 1998 to temporarily suspend the enactment of new state and local taxes on Internet access in order to encourage electronic commerce. Congress also created a committee to study the issues raised by such taxes, and to give legislative recommendations. After failing to adopt federal legislation and extending the ITFA four times, Congress finally made the act permanent in 2016.
The ITFA prohibits three types of taxes: (1) taxes on internet access; (2) discriminatory taxes on electronic commerce; and (3) multiple taxes on electronic commerce. . . . [T]he technology, business models, and charges associated with access to and use of the internet have evolved dramatically since the ITFA’s original enactment.
. . .
[T]he best solution would be for Congress to repeal or amend the ITFA to tackle the current digital economy. Otherwise, . . . ITFA could continue to lead to distortion and litigation over states' reasonable ability to tax the digital economy . . . . [T]he underlying rule the ITFA imposes is not "fit for service" and so all litigating about it is a waste of time and resources no matter the result.
intestacy law
The law that applies when someone dies without a will, with a will that is successfully challenged, or with a will that does not dispose of all of the decedent's probate estate.
intestate
Someone who dies without a will. C.f. testate.
inverted yield curve
"[Y]ields are higher on short term debt than long-term bonds . . . ." James Freeman, Paul Singer, the Man Who Saw the Economic Crisis Coming, WSJ, April 7, 2023 (Apple News link). • "An unusual situation in the bond market right now is that interest rates are higher for short-term debt than they are for long term debt. For Treasurys, that means that bills due in six months yield 4.9%, with the return declining to 3.3% in 10 years before edging back up to 3.66% in 20 years. This is called an inverted yield curve, and it predicts interest rates will decline, possibly along with economic growth, in coming years. The curve for corporates is less sharply inverted . . . ." Mitchell Martin, How Bond Laddering Can Keep You From Having An SVB Portfolio, Forbes, April 8, 2023 (Apple News link).
investment adviser
"[A] highly regulated term under the Investment Adviser Act of 1940.[A]ll investment advisers must register either with the SEC and/or by state registration and are bound by law to act as fiduciaries whether in conjunction with discretionary authority or not . . . . With a focus on investing, investment advisers don’t typically mix in financial or tax planning." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
Investment Advisers Act of 1940
"[R]egulates investment advisers including money managers, investment consultants and financial planners and requires firms and practitioners compensated for advising others about securities investments to register with the Securities and Exchange Commission." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
investment grade-rated company
A company that has a high credit rating, meaning that it has a low risk of defaulting on its debt obligations. Credit rating agencies, such as Standard & Poor's, Moody's, and Fitch, assign ratings to companies based on their financial strength, earnings potential, debt level, and debt-paying history. Companies that are rated BBB or higher by Standard & Poor's or Baa or higher by Moody's are considered investment grade. These companies are more likely to attract investors and borrow money at lower interest rates than companies with lower ratings. Investment grade companies are generally more stable and reliable than non-investment grade companies, but they may also offer lower returns and growth prospects. • Example: "Investment grade-rated companies and those with lower ratings that finally warmed to convertible bonds in 2023 after years of shunning them are set to keep the relationship going, even as investors grow increasingly convinced that central bank rate cuts are just around the corner." Amy Or, Growing Demand For Convertible Bonds Likely To Survive Rate Cuts, Financial Advisor, Jan. 9, 2024.
involuntary alienation
Involuntary alienation occurs when a person gives up title to property against their will. • Involuntary alienation can happen because of adverse possession, bankruptcy, condemnation under eminent domain, or foreclosure.
J
joint tenancy
A type of concurrent ownership where two or more people own one property interest together and each person has exactly the same rights in that interest. The interests in a joint tenancy must vest at the same time, title must be acquired through the same instrument (deed), the interests must be equal, and each tenant must have the right to possess the entire property subject to the rights of the co-tenant. • A joint tenancy may or may not have a right of survivorship. • Some states abolished joint tenancies. For example, Alaska Stat. § 34.15.130 (Join tenancy abolished) abolishes joint tenancies for real property: "Joint tenancy, with the except of interests in personalty and tenancy by the entirety is abolished. Except as provided in AS 34.15.110(b) and AS 34.77.100, persons having an undivided interest in real property are considered tenants in common." • Other states retain joint tenancy as a concurrent ownership classification but abolish the right of survivorship. Tenn. Code § 66-1-107 (Survivorship in joint tenancy abolished): "In all estates, real and personal, held in joint tenancy, the part or share of any tenant dying shall not descend or go to the surviving tenant or tenants, but shall descend or be vested in the heirs, executors, or administrators, respectively, of the tenant so dying, in the same manner as estates held by tenancy in common."
joint tenancy with right of survivorship
A joint tenancy that carries the right of survivorship, which means the property automatically goes to the surviving owner by operation of law, rather than descending to the decedent-owners' heirs or being transferred by the decedent-owner's will.
joint will
"A joint will is one instrument executed by two persons as the will of both--that is, one will for two people. When one testator dies, the instrument is probated as the testator's will; when the other testator dies, the instrument is again probated, this time as the other testator's will. A joint will is relatively uncommon; well-counseled testators do not use them. . . . [J]oint wills are notorious litigation-breeders that should not be used at all." Jesse Dukeminier et al., Wills, Trusts, and Estates (7th ed. 2005).
Juneteenth
A holiday that celebrates the emancipation of Black Americans from enslavement. • In 2021, President Joe Biden signed a law making June 19th a federal holiday. See Todd J. Gillman, Biden signs law making Juneteenth a federal holiday, marking end of slavery in Texas long after emancipation, The Dallas Morning News, June 17, 2021 (Apple News link).
junk bonds
Riskier bonds that are often issued by high-risk private companies. • "[B]onds with lower credit qualities [that] have the downside of increased credit or default risk." Paul S. Lee, Implementing Total Return Trusts (2002). • "[H]igh-yield debt with doubled-digit changes of impairment." Mitchell Martin, How Bond Laddering Can Keep You From Having An SVB Portfolio, Forbes, April 8, 2023 (Apple News link). • Also called "high-yield bonds."
jurisdiction
The authority of a court to hear and decide a case.
K
L
labor hoarding
"Employers' propensity to hold on to workers even as the economy slows . . . ." Abha Bhattarai & Lauren Kaori Gurley, Labor market adds 236,000 jobs in March, powering economy on, Washington Post, April 7, 2023 (Apple News link).
laddered bond portfolio
A portfolio of bonds that mature at different set periods (such as every year) or that have short, medium, and longer maturity. The goal is to give you access to cash when the bonds mature without having to sell the bond. If you don't need the cash, you can reinvest the proceeds in new bonds.
land trust
"A land trust is a trust of real estate wherein the settlor grants the realty to a trustee to have and to hold in fee simple. The trustee has full record title and under the terms of the deed in trust is entitled to all the rights, privileges and powers of record ownership. The deed in trust specifically states that a potential purchaser, lessee, mortgagee, or pledgee shall not be obliged to inquire into the authority of the trustee's acts. This deed in trust is subject to a second document known as a land trust agreement which enumerates the beneficiary's rights in relation to the trustee. It is important to remember, for purposes of marketability of title, that only the deed in trust is recorded. The unrecorded trust agreement lists the beneficiary's rights with respect to the property which are: 1) the power to direct the trustee to convey or otherwise deal with the title to the property, 2) the right to manage and control the property and 3) the right to receive the proceeds and avails from the rental, sale, mortgage or other disposition of the property. The important distinguishing factor between a land trust and the so-called real estate investment trust (more commonly referred to as a business or Massachusetts trust) is that in the latter, the trustee actually manages the business by making the decisions and investing accordingly. In a land trust the duties of the trustee are severely restricted by the land trust agreement to acts affecting the title to the property and those acts can only be performed at the direction of the beneficiaries. Land Trusts in New York, 37 St. John's L Rev. (1962) (footnotes omitted).
last-in, first-out (LIFO) method
"[Y]ou . . . sell the most recently purchased securities. This option may mean your capital gains portion is lower and the principal is higher. This would allow you to withdraw more while keeping your capital gains low. It is another way to keep your taxable income below the bracket if you need more money in a specific year, assuming the securities were held for more than 365 days, classifying them as long-term capital gains." Laila Maidan, How to pay 0% capital gains tax on up to $123,250 of income, Business Insider, June 22, 2024 (Apple News link). C.f. first in, first out (FIFO) method.
"laughing" heir
A distant relative of a decedent (such as a distant cousin in a foreign country), who is said to be "laughing" because the relative rejoices at receiving an inheritance, instead of feeling remorse at the loss of the decedent.
Lean FIRE
"Lean FIRE is when someone has saved up 25 times their annual expenses -- the traditional benchmark for financial independence -- and spends less each year than the average American." Tanza Loudenback, What is Fat FIRE vs. Lean FIRE? 2 different ways to retire early, Business Insider, Nov. 12, 2020 (Apple News link). "The average US household spends about $61,000 a year, according to Census data." • "The [FIRE] movement even has offshoots, with some focusing on extreme frugality and others on building a large retirement fund or keeping a part-time job. For example, Lean FIRE represents those on the extreme side of the movement who live on less than $40,000 a year." Laila Maidan & Kathleen Elkins, FIRE Movement: Early retirees discuss limitation, need to resume working, Business Insider, Sept. 13, 2023 (Apple News link). • See financial independence and FIRE movement; c.f. Barista FIRE and Fat FIRE.
legacy
"A transfer of personal property by will." NY § SCPA 103(9).
legal list state
"New York was, for a considerable period of time, a 'legal list' state, with frequent amendments. In such states the basic principle of law governing the investment of trust funds is that unless the will provides otherwise a trustee is limited to investing trust funds in certain classes of investments specified by statute and commonly referred to as 'legal investments' or 'legals.'" Jule E. Stocker et al., Stocker and Rikoon on Drawing Wills and Trusts § 6:9.3, at 6-45 (Practising Law Inst. 2011).
legal obligations of an estate
An estate's debts, taxes, charges, and claims.
legal rate of interest
"[T]he statutory interest rate that is applied to money judgments, beginning on the date of entry and ending on the date of satisfaction." Jesse Dukeminier et. al., Wills, Trusts, and Estates 818 (7th ed. 2005). See NY CPLR 5004(a) (" Interest shall be at the rate of nine per centum per annum, except where otherwise provided by statute . . .").
legatee
"Any person designated to receive a transfer by will of personal property." NY SCPA § 103(33). See also NY EPTL 13-4.1(d). C.f. devisee.
letters
NY SCPA § 103(24) defines "letters" as a category that includes (1) letters of administration, (2) letters of administration c.t.a., (3) letters of administration d.b.n., (4) limited letters of administration, (5) ancillary letters of administration, (6) ancillary letters of guardianship, (7) ancillary letters testamentary, letters of guardianship, (8) letters of temporary administration, (9) letters testamentary, (10) preliminary letters testamentary, and (11) letters of trusteeship." It further states, "A testamentary trustee who has qualified without the issuance of letters shall be deemed for the purposes of this act to have received letters of trusteeship." • NY SCPA § 103(20)(defining an executor) and NY SCPA § 103(2) (defining a fiduciary) mention "letters." • See executor, fiduciary.
life estate
A type of estate where a person (the grantee) has the right to use and enjoy a property for the duration of their life. The estate is measured by the life of the grantee.
life estate pur autre vie
A life estate that is measured by the life of someone other than the grantee. C.f. life estate.
life insurance
A type of insurance designed to provide financial security to loved ones in the event of the policyholder's death. It typically involves paying regular premiums in exchange for a lump sum payment to beneficiaries upon the policyholder's passing. The amount of coverage and premiums paid can vary based on factors such as age, health, and lifestyle. Life insurance is often purchased to ensure that loved ones are taken care of after the policyholder's death and can be used to cover expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and living expenses.
life insurance trust
"A life insurance trust is a legal entity you set up that takes ownership of your life insurance policy. Since the trust owns your life insurance policy, your estate doesn’t include the death benefit when you pass away, which helps your heirs avoid estate taxes." Taylor DeJesus, What Is a Life Insurance Trust?, Money, Sept. 2023 (Apple news link).
life settlement
A financial transaction that allows a policy owner to sell their life insurance policy to a third party for a lump sum payment. The buyer of the policy then becomes the new owner and beneficiary of the policy, responsible for paying the premiums and receiving the death benefit when the insured passes away. It can be a helpful option for individuals who no longer need or can afford their life insurance policy, or who would rather receive a lump sum payment now instead of waiting for the death benefit to be paid out.
lifetime trust
A trust created while the settlor is alive. C.f. testamentary trust.
lineal ancestors
Parents, grandparents, and great-grandparents.
lineal descendants
Sons, daughters, grandchildren, great-grandchildren, etc.
liquid asset
An asset that can be readily converted into cash. Examples: A checking or saivngs account.
loan principal
The amount of money that is being borrowed in a loan.
loan-to-value ratio
The amount being borrowed in a loan divided by the appraised value for the property. See David McMillin, What is a loan-to-value ratio?, Bankrate, June 27, 2023 (Apple News link) ("From a lender’s perspective, a lower LTV ratio is better than a higher one because it indicates that a loan applicant can make a larger down payment and won’t have to borrow as much money.").
longevity risk
The problem of outliving retirement savings. Because people don't know how long they're going to live, there is uncertainty in building a nest egg that will last their life-span. • "People tend to underestimate their lifespan when planning for the future, advisers said. A 65-year-old woman today who is a nonsmoker and in excellent health has a 54% chance of living to 90, a 31% chance of living to 95 and a 13% of living to 100, according to the Actuaries Longevity Illustrator." Ashlea Ebeling, A Retirement Tax Break That Ends the Fear of Outliving Your 401(k), WSJ, July 23, 2023 (Apple News link).
long-term care insurance
Insurance that covers the costs of long-term care, such as the cost of a home health aide to assist with some of the activities of daily living. • "Unlike health insurance, which typically has policy limits that renew each year, long-term care insurance policies instead provide coverage for a set number of years once qualifying events occur. So, choosing fewer years of coverage can lower long-term care insurance's price." Jake Safane, Buying long-term care insurance in your 70s? Do this to keep costs down, experts say, CBS News, June 19, 2024 (Apple News link).
loophole
A way of avoiding a tax that is intentionally provided by Congress or discovered by creative lawyers.
lord
In feudal England, the owner of a manor. • "Not only did the lord supervise the agricultural economy of the manor, but he also, through the manorial courts over which he presided in person or through his bailiff, adjudicated controversies among his tenants and regulated much of their daily lives." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 13 (7th ed. 2020). • The lord had free tenants who held land in socage or by knight service. The lord retained the remaining lands (demesne lands), which the villeins worked. • A lord presided over two courts: the Court Baron (for free tenants) and the Court Customary (for villein tenants).
Lucas v. Earl, 281 U.S. 111 (1930)
A landmark U.S. Supreme Court decision that held that taxpayers -- in this case, spouses -- cannot avoid income tax by assigning their income to others. Fruits must be attributed to the tree on which they grew, not "a different tree from that on which they grew."
M
managed account
See separately managed account.
manor
In feudal times: An estate or unit of lordship, varying in size. • "The manor was an agricultural, governmental, and fiscal unit, usually co-extensive in territory with the ancient village, composed of lands held by the lord and by tenants of different classes." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 13 (7th ed. 2020). • See lord.
manorial court
In feudal times, a court presided over by a lord (or the lord's bailiff) that adjudicated disputes among tenants. • The lord presided over two manorial courts: The Court Baron for free tenants, and the Court Customary for villein tenants. • Villein tenants had recourse only in the manorial courts, not the royal courts.
marginal tax rate
"A marginal tax rate is a tax rate based on the last dollar of taxable income. . . . The U.S. and many countries use such a tax bracket system in which a different tax rate is applied to different levels of taxable income. As a person’s income increases, so does the marginal tax rate. . . . Marginal tax rates do not take into account payments for Social Security and Medicare. Those are deducted separately." TheStreet Staff, What Is a Marginal Tax Rate? Definition & Example, TheStreet, May 24, 2023 (Apple News link).
market risk
Risk that "is common to all securities; it reflects general economic and political conditions, interest rates, and so forth." John H. Langbein, The Uniform Prudent Investor Act and the Future of Trust Investing, 81 Iowa L. Rev. 641, 647 (1996). C.f. firm risk and industry risk. Risk that is "unavoidable in investing" and is "compensated by expectations of increased return. [There is a] direct relationship between market risk and portfolio return expectations." Restatement 3d Trusts: Prudent Investor Rule.
market value of a bond
The amount at which a bond is currently trading. • A bond's market value falls when interest rates rise. See Jonathan Weil, Risking Interest Rates Hit Banks' Bond Holdings, WSJ, Nov. 11, 2022 (Apple News link). • C.f. book value of a bond.
marketable title
Title that has no defects. C.f. insurable title.
mass affluent
"[M]iddle-class households with between $100,000 and $1 million in investible assets." Lori Ioannou, Brokerage Firms Are Pitching Separately Managed Accounts. Here's What to Know., WSJ, Jan. 7, 2024 (Apple News link).
maturity
For a bond: The date on which a bond investor is repaid the original principal • "When the bond reaches maturity, the loan amount, or principal, is returned to you, the investor." Penelope Wang, 8 Things You Need to Know About Bonds, AARP Bulletin, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link).
may
In a statute or a contract, a term that indicates that performance is discretionary (not mandatory). • NY SCPA 103(38) gives this definition for "may": "When used in this act, in relation to an act to be performed by the court, means in the discretion of the court."
measuring life
For purposes of the rule against perpetuities: An identifiable person who is alive at the time that an interest in trust is created.
mediator
A mediator is a professional, neutral person who is trained to help litigants come to an agreement about their dispute without the need for a judge to decide it.
Medicaid Asset Protection Trust (MAPT)
An irrevocable trust that allows individuals to protect their assets from Medicaid after any applicable look-back period, ensuring they can receive assistance with long-term care without depleting their hard-earned resources.
Medicare Part B
"covers doctor visits and other forms of outpatient care . . . . Next year, the standard Part B premium is slated to rise by $9.90 to $174.80 a month, according to estimates Medicare’s trustees released in March." Anne Tergesen, Social Security Benefits Will Go Up Next Year, but Not by a Lot, WSJ, Aug. 10, 2023 (Apple News link).
merger
"It is a universal rule that when the purpose of a trust has been fully accomplished, the title or estate of the trustee is at an end, and if he is also entitled to the beneficial estate, the two estates meeting in the same person are merged, and he becomes vested in his own right with the entire interest in the property." Blood v. Kane, 130 N.Y. 514 (1892). • Merger can occur in the context of trusts. New York allows a settlor to be both the sole trustee and a beneficiary provided there is at least one other beneficiary, EPTL 7-1.1; but when the settlor is both the sole trustee and the sole beneficiary, merger occurs -- the trust is defeated and title to the trust estate vests in the settlor's personal name. The ability for the settlor to name even just one remainder beneficiary that takes after the settlor dies facilitates the creation of revocable lifetime trusts. EPTL 7-1.1 (when trusts interest not to merge) provides: "A trust is not merged or invalid because a person, including but not limited to the creator of the trust, is or may become the sole trustee and the sole holder of the present beneficial interest therein, whether such interest be vested or contingent, present or future, and whether created by express provision of the instrument or as a result of reversion to the creator's estate." • Merger can also occur in the context of wills with respect to personal property passing under the will after a sole executor, who is also sole devisee and legatee, pays the estate's creditors, or after the such executor assents to the executor's own legacy. Blood v. Kane informs: "The trust estate of a sole executor, who is also the sole devisee and legatee, is solely for the benefit of the testator's creditors, and when they are paid the trust estate sinks into and is merged with the beneficial interest, and the sole devisee and legatee becomes vested with the legal title of all of the testator's estate."
mesne profits
Profits from real property received by someone who is in wrongful possession. • A real property owner who succeeds in a common-law action of ejectment can bring a lawsuit seeking the profits from the use of the land while it was wrongfully occupied and the costs of ejectment. This action is known as an "action for mesne profits," "action of trespass for mesne profits," or "action for the recovery of mesne profits." See, e.g., Combs v. Jackson, 2 Wend. 153 (N.Y. 1828).
midtier millionaires
A category of high-net-worth individuals "with $5 million to $30 million" in investible assets. Quentin Fottrell, 'We've never seen this before': Millionaires are doing something unusal to preserve their wealth -- and you can do the same, MarketWatch, June 28, 2023 (Apple News link). • C.f. "millionaires next door" and ultra-high-net-worth individuals.
military tenure
In feudal times, land holding from a lord in exchange for a military service to that lord, which was an obligation of a tenant to supply a specified quota of knights to the lord or to make a monetary payment to hire knights. • Also termed, "tenure by knight service." • See tenure. C.f. serjeanty tenure.
"millionaires next door"
A category of high-net-worth individuals "with $1 million to $5 million in investible assets . . . ." Quentin Fottrell, 'We've never seen this before': Millionaires are doing something unusal to preserve their wealth -- and you can do the same, MarketWatch, June 28, 2023 (Apple News link). • C.f. midtier millionaires and ultra-high-net-worth individuals.
mistaken reversal
A logical fallacy that confuses sufficient and necessary conditions and occurs when someone "flips" the two sides. Example: The original statement is "A+ --> Study." Incorrect inference: "Study --> A+."
modern portfolio theory
States that higher risk investments must offer a higher return to compensate the buyer for assuming the additional risk. It emphasizes diversification to offset risks and maximize returns. In an efficient market, the tradeoff of risk and return is already reflected in a tradable security's price. • "By modern portfolio theory I mean the loose amalgam of academic theories that focuses investors on risk, diversification, transaction costs, and the total return of a portfolio rather than individual investments." Joel C. Dobris, Probate World at the End of the Century: Is a New Principal and Income Act in Your Future, 48 Rec. Ass'n B. City N.Y. 280 (1993).
money market fund
money market mutual fund (MMMF)
A type of mutual fund that tries to keep its net asset value at a stable $1.00 per share (using special pricing and valuation conventions) and generates interest income, but it is not FDIC-insured. • "Unlike a 'money market deposit account' at a bank, money market funds are not federally insured," but they have "relatively low risks compared to other mutual funds and most other investments and historically has had lower returns. Money market funds invest in high quality, short-term debt securities and pay dividends that generally reflect short-term interest rates. Many investors use money market funds to store cash or as an alternative to investing in the stock market." Money Market Fund, investor.gov.
monospaced typeface
A typeface where "each letter occupies the same amount of space on a horizontal line of text. . . . Courier . . . is a monospaced typeface." Supreme Court of the State of New York, Appellate Division: Second Judicial Department, A Glossary of Terms for Formatting Computer-Generated Briefs, with Examples. C.f. proportionally spaced typeface.
mortgage insurance premium
A recurring monthly payment that borrowers must pay when obtaining a Federal Housing Administration mortgage. "Because FHA mortgages allow for down payments as low as 3.5% for borrowers with a credit score as low as 580, mortgage insurance is required for all FHA home loans." Victoria Araj, What Is A Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP)?, Quick Loans, Aug. 5, 2020. C.f. private mortgage insurance.
mortgage protection insurance
Insurance to pay a mortgage or any remaining debts after the insured dies. It "is simply a small term life insurance policy," explains Kelly Maxwell in Mortgage Protection Insurance For Seniors (2022 Update), Seniors Mutual, Aug. 23, 2022. The age limit for mortgage protection insurance is age 80.
mortgage recasting
A way to prepay a portion of a qualifying mortgage by getting a bank to accept a lump-sum payment that reduces the loan's principal, which reduces monthly loan payments and interest payments over the remaining life of the loan, but keeps the loan's interest rate, duration, and other terms.
motherhood penalty
"Mothers in the workforce experience additional disadvantage compared to women who are not mothers, including a per-child wage penalty. The 'motherhood penalty' may account for a significant proportion of the gender gap in pay, as the pay gap between mothers and non-mothers could in fact be larger than the pay gap between men and women. Mothers also face additional disadvantages compared to childless women and men." Gender Action Portal, Getting a Job: Is There a Motherhood Penalty?, Harvard Kennedy School: Women and Public Policy Program; see Mary Beth Ferrante, What Your Working Parents Aren't Telling You -- And Why Not Knowing Is Costing You, Forbes, Feb. 2, 2023 (Apple News link) ("Society has normalized the belief that when it comes to being a good employee, having a child or being a caregiver is more of a mark against us than proof of our abilities. This perception is often disproportionately placed on women as evidenced by the 'motherhood penalty' and its series of disadvantages.").
motion to dismiss
A request by a party to end a lawsuit before it goes to trial, usually based on some legal defect or deficiency in the case.
municipal bond
A bond that is issued by city or state governments.
multiple dwelling
NY MDL § 4(7) defines a "multiple dwelling" as "a dwelling which is either rented, leased, let or hired out, to be occupied, or is occupied as the residence or home of three or more families living independently of each other. On and after July first, nineteen hundred fifty-five, a 'multiple dwelling' shall also include residential quarters for members of personnel of any hospital staff which are not located in any building used primarily for hospital use provided, however, that any building which was erected, altered or converted prior to July first, nineteen hundred fifty-five, to be occupied by such members or personnel is so occupied on such date shall not be subject to the requirements of this chapter only so long as it continues to be so occupied provided there are local laws applicable to such building and such building is in compliance with such local laws. A 'multiple dwelling' shall not be deemed to include a hospital, convent, monastery, asylum or public institution, or a fireproof building used wholly for commercial purposes except for not more than one janitor's apartment and not more than one penthouse occupied by not more than two families. For the purposes of this chapter "multiple dwellings" are divided into two classes: 'class A' and 'class B.'" • See dwelling.
N
natural burial
Burial "in which a body is buried without a coffin or with a biodegradable coffin." James FitzGerald, New York approves composting of human bodies, BBC News (Apple News link). • Natural burials are permitted in the United Kingdom. Id.
N.B.
See nota bene.
net asset value
The bottom-line value of a fund's assets divided by the number of outstanding shares.
net investment income tax (NIIT)
"It’s a 3.8% surtax on a filer’s income from sources like interest, dividends and capital gains that applies if adjusted gross income, or AGI, is above $200,000 for most single filers or $250,000 for most married couples. It affects one-time spikes as well as recurring income, so taxpayers who typically earn less can owe it on a windfall." Laura Saunders, The 'You-Make-a-Lot-of-Money Tax' Hits More Americans, WSJ, June 23, 2023 (Apple News link).
net pay
An employee's earnings after payroll deductions are subtracted from gross pay. C.f. gross pay.
net sales
The total revenue generated by a business over a certain period of time, after accounting for any discounts or returns. It is essentially the money a company receives from selling its products or services. C.f. profit. See Hani Sarji, Net Sales v. Profit, Wills, Trusts, Estates, Aug. 7, 2023.
New Domesday Book
A survey of land ownership in Great Britain conducted in 1874, nearly 800 years after the first. See Domesday Book.
next of kin
At common law, next of kin inherited personal property. See Jones v. Kelly, 13 N.E. 443 (N.Y. Ct. Appeals 1902).
NFTs
See nonfungible tokens.
nominal consideration
In a deed, a statement that says that a property is being conveyed for "One dollar and other good or valuable consideration." Often, deeds with nominal consideration also read, "Ten dollars and other good or valuable consideration." • In New York, reciting nominal consideration is common because a deed must provide evidence of consideration, but it does not have to recite the actual amount of consideration involved.
non dat qui non habet
The principle that an individual may convey no better title to an item of property than that which the individual possesses. • "It is the primary rule of common law, which possesses substantially universal applicability, that an individual may convey no better title to an item of property than that which he himself possesses. This is compressed in legal terminology to the familiar phrase 'non dat qui non habet'." In re Goodchild, 160 Misc. 738 (N.Y. Surrogate's Ct., Kings. Co. 1936).
non-discretionary fiduciary financial adviser
A fiduciary role in which an adviser manages investments but must first get the client's permission before each transaction.C.f. discretionary fiduciary investment adviser.
nonfungible tokens
"NFTs are bitcoin-like tokens connected to a digital work of art or other real-world item and sold as a unique digital item." Paul Vigna, DeFi Is Helping to Fuel the Crypto Market Boom -- and Its Recent Volatility, WSJ, June 3, 2021 (Apple News link).
non-grantor trust
A trust that is taxed as a separate taxpayer. because the grantor is not deemed to be the owner of the trust corpus for tax purposes. C.f. grantor trust.
non-judicial settlement of an estate
"The informal or non-judicial settlement of an estate permits the executor or administrator to wind-up the administration of the estate, make final distribution, and be released from liability for his actions by agreement with the parties, with no or only limited involvement by the court. . . . The term "informal" is generally taken to refer to the manner in which the account is settled. It may also refer to the account itself. Because an informal settlement does not contemplate judicial review or approval of the account, there is no requirement that the account be in any particular form. Indeed, the account need not even be filed with the court." Susan B. Reuben, Informal Settlement of Estates, NYSBA course book, Fall 2020.
nonmatching contributions
Employers "put money into [a retirement] account on behalf of eligible employees whether or not they are saving themselves. These often take the form of fixed- or variable-rate profit-sharing payments." Jeanne Sahadi, New report flashes a warning over 401(k) account balances, CNN Business, June 15, 2023 (Apple News link).
non-probate asset
See will substitute.
normalcy bias
Underestimating the likelihood and impact of a disaster or crisis.
Norman Conquest
The Normans' defeat of the Saxons in 1066, which changed England's ruling class and system of land holding. • The Norman Conquest introduced military tenure into England.
nota bene
Latin for "mark well" or "take note." • An indication that what follows is particularly important. • Abbreviated as "N.B."
notice of appeal
A document that informs the court and the other parties that one party in a lawsuit intends to appeal a decision or judgment made by a lower court.
nullius in verba
Latin for "don't take anyone's word for it." This is the motto for the London-based Royal Society, which is the ancestor of the research university. See James Hankins, Opinion: Claudine Gay and Why Academic Honesty Matters, WSJ, Dec. 27, 2023 (Apple News link).
O
obiter
A part of a judicial opinion that is not necessary to deciding the case at hand. It is not binding on subsequent cases, but is considered persuasive. • Example: "The question was considered by Judge Grover in Juliand v. Rathbone (39 N.Y. 369), but it was not necessary to decide it as the judgment was necessarily as given, whether the court held the one way or the other on the point now under consideration. The remarks of the learned judge upon that branch of the case did not necessarily embody the views of the court and may be regarded as obiter, and the judgment as passing upon the other ground suggested by him." Brennan v. Willson, 71 N.Y. 502 (1877).
occupant
"[A] person, other than a tenant or a member of a tenant's immediate family, occupying a premises with the consent of the tenant or tenants." NY RPL § 235-f.
off-the-rack rule
See default rule.
off-the-shelf rule
See default rule.
order
A decision or direction of the court that does not resolve the entire case but decides an issue or directs some action before the final judgment. C.f. final judgment.
ostrich effect by investors
"When stock are down, many investors avoid unpleasant news, in what is known as the ostrich effect . . . ." Anne Tergesen, Why a Bull Market Is a Bad Time to Check Your 401(k), WSJ, June 15, 2023 (Apple News link).
overreaching
Situations where one party takes unfair advantage of another, typically through deceptive or manipulative practices, which deprive the other party of their free will. Overreaching is often used synonymously with coercion or duress. See 🔑 NY: Stipulations Can Be Set Aside Because of Overreaching].
P
part performance
An equitable exception the Statute of Frauds by which courts enforce oral contrast relating to real estate. • Pattelli v. Bell, 187 Misc.2d 275, 721 N.Y.S.2d 734 (Supreme Ct., Richmond Co. 2001):
Part performance "is based on principles of equity, and, specifically, recognition of the fact that it would be a fraud to allow one party to a real estate transaction to escape performance after permitting the other party to perform in reliance on the agreement" (Messner Vetere Berger McNamee Schmetterer Euro RSCG v Aegis Group, 93 NY2d 229, 235; see General Obligations Law § 5-703 [4]). Part performance alone is not enough. "There must be performance 'unequivocally referable' to the agreement, performance which alone and without the aid of words of promise is unintelligible or at least extraordinary unless as an incident of ownership, assured, if not existing" (Burns v McCormick, 233 NY 230, 232). "What is done must itself supply the key to what is promised. It is not enough that what is promised may give significance to what is done" (id.).
partnership
An unincorporated organization with two or more members.
passive trust
A trust in which the trustee has no duties. C.f. active trust.
pass-through entity tax (PTET)
Allows partnerships and S corporations to elect annually to pay state and local taxes through the entity and for the partners and shareholders to receive a personal income tax credit equivalent to the tax that the entity paid. See N.Y. Tax Law §§ 860, 861. • Some states, such as New York, enacted the PTET as a response to the state and local tax cap of $10,000 that the Tax Cut and Jobs Act of 2017 imposed. • On April 9, 2022, New York City became the first city in the United States to enact a PTET (retroactive to January 1, 2022). N.Y. Tax Law Article 24-B.
patrimony
An inheritance from one's father or ancestor of the father. • Example: "On some undisclosed previous date each [infant] had received as a legacy from a grandmother two $1,000 bonds . . . . [Because of a wrongful transfer of the legacy by the father of infants, the] court is . . . confronted with the unwelcome alternative of determining either that the patrimony of the infants is lost to them, or that the respondent, who admittedly paid value and had no notice of the facts hereinbefore recited, must refund the proceeds or value of the securities." In re Goodchild, 160 Misc. 738 (N.Y. Surrogate's Ct., Kings. Co. 1936) (emphasis added).
pay-as-you-go
See pay-go.
pay-go
"[A] budgeting mechanism . . . short for 'pay-as-you-go', that says new legislation or executive orders affecting revenues and spending on Medicare, social security and other key programs must be budget-neutral." Guardian staff and agency, Biden, McCarthy agree to raise US debt ceiling - what's in the deal?, The Guardian, May 28, 2023 (Apple News link).
pecuniary distribution
A distribution of a set dollar amount, not a percent or an in-kind distribution.
pension fund
"[P]ension funds . . . manage retirement savings for public employees." The Wealth Advisor, Trump's Executive Order For A US Sovereign Wealth Fund: What Could That Mean, Feb. 5, 2025.
persistence bias
The cognitive tendency to assume that the current state of affairs will continue into the future, despite potential evidence or reasons to expect change. It's a form of status quo bias or projection bias, where people overestimate the stability or continuity of systems, conditions, or trends.
Personal Consumption Expenditures Index (PCPI)
"[T]he Federal Reserve's preferred measure of inflation . . . ." Protect Your Wealth Against Inflation in Three Easy Steps, Kiplinger, Dec. 15, 2023 (Apple News link). The PCEPI is a measure of the prices that people living in the United States, or those buying on their behalf, pay for goods and services. The PCEPI is known for capturing inflation (or deflation) across a wide range of consumer expenses and reflecting changes in consumer behavior.
petit serjeanty
In feudal times, a type of serjeanty tenure that "involved services of a humbler nature" than grand serjeanty, "such as providing military supplies or other articles of small value." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 11 (7th ed. 2020). • "[W]ardship" was incident to grand serjeanty, but not to petit serjeanty . . . ." Id. at 31 n.24.
petition
A formal, written application to a court requesting a judicial decision.
petition for a writ of certiorari
" In a typical year, lawyers file 7,000 to 8,000 petitions for a writ of certiorari, the formal name for a petition asking the Supreme Court to give full review to a lower court’s order. The Court typically grants fewer than 80 of these 'cert' petitions." Ian Millhiser, The Supreme Court's enigmatic 'shadow docket,' explained, Vox, Aug. 11, 2000 (Apple News link).
plaintiff in error
See appellant.
point size
"[A] unit of measurement used by printers equal to approximately 1/72 of an inch. The vertical height of type is measured in points. The measurement is somewhat complicated and requires a special ruler. The process of measurement is well explained in The Chicago Manual of Style (14th ed.) § 19.43. Suffice it to say that an attorney or litigant may rely on the type size setting of the word processing program used to create the brief. A brief utilizing a proportionally spaced typeface must use 14-point type for the body of the text, but 12-point type may be used for footnotes. A brief utilizing a monospaced typeface must use 12-point type for the body of the text, but 10-point type may be used for footnotes." Supreme Court of the State of New York, Appellate Division: Second Judicial Department, A Glossary of Terms for Formatting Computer-Generated Briefs, with Examples.
poll tax
A term that "often refers to a very specific tactic of white supremacy: the use of tax policy to prevent voting by Black citizens." Jeremy Bearer-Friend, Race-Based Tax Weapons, 14 U.C. Irvine Law Review __ (forthcoming 2023) (SSRN link).
portfolio manager
"[S]omeon who handles investing strategies and decisions on behalf of their clients . . . ." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
postponed power of appointment
A power of appointment that "is exercisable by the donee only after the expiration of a stated time or after the occurrence or non-occurrence of a specified event.” [EPTL 10-3.3(d)](http://(https//www.nysenate.gov/legislation/laws/EPT/10-3.3).
pour-over will
A will that transfers ("pours") the decedent's assets to a living trust.
power
"A power is the authority to do any act in relation to property (EPTL 10-2.1). . . . A power is not an estate or interest in land, but an authorization to create an estate in land. The power may be given to a party with no beneficial interest in the land (Root v. Stuyvesant, 18 Wend 257). The power includes the power to revoke the previous estate (Chamber v. Kelsey, supra.)." Estate of Edwards, NYLJ Feb. 18, 2020 at 30, col. 2 (Sur. Ct. Kings County 2000, Sur. Feinberg).
power of appointment
The right to designate who will possess or enjoy property.
power of attorney
A document in which one person (the principal) empowers one or people (the agent) to make specified financial decisions on the principal's behalf.
precatory language
Non-binding language in a will or trust, such as "I wish," "I hope," or "I desire."
predecease
To die before.
present interest
An estate in land to which the holder is currently entitled to possession. C.f.future interest.
preservation planning
Planning that focuses on preserving assets for the duration of an individual's retirement, with the possibility of benefiting loved ones during life or upon death. • For example, a financial advisor might create a wealth preservation plan that allows an individual to live off retirement assets while making annual gifts to children. See estate planning.
presumption
"A presumption has been defined as a rule of law 'which requires that a particular inference must be drawn from an ascertained state of facts'." Prince, Richardson on Evidence § 3-101, at 53 (Farell 11th ed rev), qtd in Matter of Ives](https://scholar.google.com/scholar_case?case=9655742036549118864&q=Ives,+745+N.Y.S.2d+904&hl=en&as_sdt=4,33), 192 Misc. 2d 479 (NY Sur. Ct., Broome Co. 2002).
primer seisin
See relief.
primogeniture
The common-law rule that land descended to the oldest son on the owner's death. C.f. burgage tenure, gavelkind tenure.
principal
For a bond: The amount of money which a bond investor loans to a borrower.
principal-agent problem
When an agent acts in the agent's best interest interest, rathther than the best interest of the principal.
private mortgage insurance
A recurring monthly payment that borrowers must pay when obtaining a conventional mortgage, but only when they are making a down payment smaller than 20% of a home's value. C.f. mortgage insurance premium. • "PMI, which is arranged through a third-party insurance company, is designed to protect the lender if you’re unable to make payments. PMI doesn’t protect you against loss — if you don’t make payments, you could still face foreclosure — and it won’t prevent your credit score from dropping if your mortgage payments are late." Ella Vincent, What is Private Mortgage Insurance and How Does It Impact Buying a Home?, Kiplinger, June 19, 2024 (Apple News link).
private trust company
"A private trust company, also known as a family trust company, is an entity formed and authorized under state law to act as a fiduciary for a single family, and it is prohibited from transacting business with the general public. Family members are typically defined under state law by their degree of kinship to a designated relative, such as patriarch or a matriarch. Depending on applicable state law, a private trust company can be formed as a limited liability company or a corporation." Jim Weller, The Private Trust Company Solution, LISI Webinar, June 13, 2023.
probate
The process by which a will is given effect after death.
probate assets
Assets that are controlled by a will.
probate estate
"A probate estate includes only assets that pass through a will." Gross Estate vs. Probate Estate, Smart Asset, July 28, 2023. C.f. gross estate.
profit
The amount of money that a business earns after deducting all of its expenses from its revenue. Expenses include operating costs, taxes, and any other expenses that the business may incur in the process of generating revenue. C.f. net sales. See Hani Sarji, Net Sales v. Profit, Wills, Trusts, Estates, Aug. 7, 2023.
progressive tax
A tax that imposes a larger share of the tax burden on those who have more or earn more. It imposes lower tax rates on lower-income taxpayers and higher tax rates on higher-income taxpayers. See TheStreet Staff, What Is a Progressive Tax? Definition & Example, May 24, 2023 (Apple News link) ("A progressive tax structure allows low-income earners to pay a smaller proportion of their income as tax compared to high-income individuals, who are taxed at progressively higher rates."). C.f. flat tax, regressive tax.
projection bias
Believing that future preferences or conditions will align with the present.
proportionally spaced typeface
A typeface "designed so that the amount of horizontal space each letter occupies on a line of text is proportional to the design of each letter, the letter i, for example, being narrower than the letter w. More text of the same type size fits on a horizontal line of proportionally spaced type than a horizontal line of the same length of monospaced type. . . . Times New Roman . . . is a proportionally spaced typeface." Supreme Court of the State of New York, Appellate Division: Second Judicial Department, A Glossary of Terms for Formatting Computer-Generated Briefs, with Examples. C.f. monospaced typeface.
pro tanto
To that extent. • Example: "[T]he wearing apparel remained a part of the assets of the estate and, having been turned over to and accepted by the objectant, must be deemed a pro tanto satisfaction of her distributive rights, with the resultant reduction of the sum to which she is entitled to $ 126.99." Estate of Williams, 295 N.Y.S. 56 (Sur. Ct., Kings Co. 1937) (emphasis added).
PTET
An acronym that stands for "pass-through entity tax".
public record
A record created by a government in the normal course of its business.
purposivist
In statutory interpretation: "[P]urposivists seek to discern a statute's purpose(s). See, e.g., Henry M. hart, Jr. & Albert M. Sacks, The Legal Process: Basic Problems in the Making and Application of Law 1374 (William N. Eskridge, Jr. & Philip P. Frickey eds., 1994) (instructing interpreters to '[d]ecide what purpose ought to be attributed to the statute and to any subordinate provision of it'); Robert A. Katzmann, Judging Statutes 31 (2014) ('The task of the judge is to make sense of legislation in a way that is faithful to Congress's purposes.'); [Kevin M. Stack, Interpreting Regulations, 111 MICH. L. REV. 355, 387 (2012)] (making a similar argument as to Congress's formal statements of purpose)." Gregory A. Elinson & Robert H. Sitkoff, When a Statute Comes with a User Manual: Reconciling Textualism and Uniform Acts, 71 Emory L.J. 1073 (2022). C.f. intentionalist.
put
A financial contract that gives an investor the ability to sell an asset for a set price. • A put is a bet that the asset will trade lower. So, it is considered a bearish contract. • C.f. call.
Q
qualified charitable distribution (QCD)
"A QCD is a direct transfer of funds from an IRA to a qualified charity. QCDs can be counted toward satisfying one’s RMDs, but, unlike regular withdrawals from an IRA, the donor doesn’t pay tax on these dollars. This will help keep a retiree’s taxable income lower, since the distribution doesn’t count toward adjusted gross income. The maximum annual amount that can qualify for a QCD is $100,000." Jonathan I. Shenkman, Retirees Have to Pay Taxes, Too. 6 Smart Ways to Reduce Them., Barron's, Nov. 22, 2023 (Apple News link).
Qualified Terminable Interest Property Trust (QTIP)
A trust that "allows an individual to leave assets to a surviving spouse along with specific instructions to pay out the remaining assets upon the surviving spouse’s death. The surviving spouse doesn’t have the ability to make changes to how the remiander is paid out . . . ." Debbie Carlson, A Will Can Split a Family. How to Avoid the Hurt., Barron's, July 15, 2023 (Apple News link).
quantitative easing
"Quantitative easing expands the money supply—when the Fed purchases Treasuries and other securities directly from banks and on the open market, it creates money out of thin air to do it. That new cash ends up on bank balance sheets, which they can then use to increase lending to businesses and consumers. The greater availability of credit contributes to lower interest rates, more economic activity, and higher asset prices." Nicholas Jasinski, Saving the Banks Isn't Quantitative Easing, Barron's, March 20, 2023 (Apple News link). • "Since the 2008 crisis, the fed and other central banks have undertaken various rounds of 'quantitative easing' -- creating money to buy government bonds and other assets. The artificial demand for such assets holds down interest rates, which enables political authorities to spend lavishly, run massive deficits and take countries deeper into debt." James Freeman, Paul Singer, the Man Who Saw the Economic Crisis Coming, WSJ, April 7, 2023 (Apple NEws link). • "The Fed has taken some of [Silicon Valley Bank's] losses onto its own balance sheet, and that is in effect a resumption of quantitative easing. There will be more money printed at just the time the Fed was meant to be fighting inflation." Matthew Lynn, Bank collapse spells higher inflation, Money Week, March 2023 (Apple New link).
quantitative tightening
"After the spread of the Covid-19 pandemic, the U.S. central bank made enormous purchases of Treasurys and mortgage-backed securities in 2020 to stabilize financial markets. In June 2022, the Fed initiated a program to reverse this process, passively shrinking those holdings by allowing securities to 'runoff' the portfolio without replacing them with new ones, a process known as quantitative tightening. // This allowed up to $60 billion in Treasurys and up to $35 billion in mortgage-backed securities to mature monthly without reinvesting the proceeds." Alice Uribe, Perpetual Sells Bonds, Cuts Cash as Fed Slows Pace of Quantitative Tightening, WSJ, June 20, 2024 (Apple News link).
R
Rashomon effect
The phenomenon where different people have contradictory interpretations of the same event, highlighting the subjective nature of perception and memory.
ratio decidendi
The rationale of a decision; the legal basis of a decision.
reacquired stock
See treasury stock.
real estate
See real property.
real property
Land and any permanent structures on it. • Real property is commonly known as "real estate."
realization
"[A]n identifiable event before accrued income is reportable by taxpayers." Sloan G. Speck, The Realization Rule as a Legal Standard, 16 Colum. J. Tax. L. __ (forthcoming 2024) (SSRN link).
Receipt and Release Agreement
A legal document that contains a summary of the events of an estate administration from the date of death to the closing of the account and that is reviewed and signed by the interested parties at the time the estate was closed, who acknowledge receipt of all property to which each party is entitled, and who agree "to release the executor from all liability with respect to the administration of the estate, to indemnify the executor against any expenses or claims which may at any time be asserted against the executor, and to refund to the executor any amount of such party's total distribution which is either needed to so indemnify the executor or later discovered to be an overpayment to such party." Susan B. Reuben, Informal Settlement of Estates, NYSBA course book, Fall 2020. • This document is sometimes called a "Receipt, Release, Refunding and Indemnification Agreement" or "Agreement Settling Account."
Receipt, Release, Refunding and Indemnification Agreement
See Receipt and Release Agreement.
recession
"[A] recession is a general decline in a country's production of goods and services, measured usually as two consecutive quarters of shrinking growth as determined by the National Bureau of Economic Research." Caitlin Ostroff, The Dow Is Officially in a Bear Market. Here's What to Know., WSJ, Sept. 26, 2022 (Apple News link).
record date
The record date is the date on which a company reviews its books to determine which shareholders are eligible to receive the upcoming dividend payment. In order to receive the dividend, shareholders must be on the company's books as of the record date. For example, if a company declares a dividend with a record date of May 1 and you own shares in the company on or before May 1, you will be eligible to receive the dividend payment.
regressive tax
A tax that imposes higher tax rates as income decreases. C.f. flat tax, progressive tax.
reinvestment risk
"[T]the risk of having to reinvest a maturing bond at a lower interest rate in the future. Essentially, these currently high yield levels [on short-term Treasuries and money market accounts] are fleeting and likely won’t be as high down the line when your bond matures and you want to reinvest your money." Lisa Scherzer, Bonds Are a Great Buy Now. How to Protect Yourself., Barron's, Aug. 19, 2023 (Apple News link).
remaining executor
The executor where there are two or more executors, and one or more renounce.
relief
In feudal times, a sum paid by a deceased tenant's heir to the lord for the privilege of succeeding to the decedent's lands. • The relief "functioned as a sort of feudal inheritance tax. Inheritance was a privilege to be paid for, not an unconditional right." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 16 (7th ed. 2020). • "Payment of the relief by the heir of a subtenant entitled the heir to immediate possession, but on the death of a tenant-in-chief, the king, by royal prerogative, was entitled to first seisin (primer seisin) of all the deceased tenant's lands, not only those held directly of the king, but also those held of mesne lords. Only after an official inquest to determine heirship, the doing of homage, and the payment of the relief was the heir admitted to seisin or possession." Id. Relief was an incident of tenure.
remedy of distress
In medieval England, a lord who was not provided a service owed by a tenant had the right to seize any chattels found on the land.
remote-ink notarization (RIN)
A notary's witness of documents via live audiovisual technology. It is "remote-ink" because wet ink notarization of paper documents is required. So, the witnessing is not completely electronic. C.f. remote online notarization.
remote online notarization (RON)
A notary's witness of documents via live audiovisual technology. It is "online" because the witnessing is completely electronic; wet ink notarization of paper documents is not needed. C.f. remote-ink notarization.
rent
"[T]he monthly or weekly amount charged in consideration for the use and occupation of a dwelling pursuant to a written or oral rental agreement." NY RPAPL § 702.
renunciation
See disclaim.
required beginning date
The first date the original retirement account owner was required to begin taking required minimum distributions.
required minimum distribution (RMD)
For certain retirement accounts, the amount an individual must take. • RMDs "are the bare minimum one is required to take. If someone is in an advantageous tax situation, taking more than what is required can minimize taxes on the distributions later." Jonathan I. Shenkman, Retirees Have to Pay Taxes, Too. 6 Smart Ways to Reduce Them., Barron's, Nov. 22, 2023 (Apple News link). • "RMDs are the government’s way of getting its share of retirement savings that has grown tax-deferred for decades." Elizabeth O'Brien, 20% of Retirees Haven't Taken Their RMD. What Happens if You Miss the Deadline., Barron's, Dec. 14, 2023 (Apple News link).
res
Trust property.
res judicata
"[R]es judicata precludes a party from asserting a claim that was litigated in a prior action (see, Parker v Blauvelt Volunteer Fire Co., 93 NY2d 343, 347)." People v. Evans, 94 N.Y.2d 499 (2000).
restricted document
Respecting New York WebSurrogate: A document that is listed on WebSurrogate but inaccessible because a link is not available. • Documents that have personal identifiers, like a Social Security number, would get restricted. For example, a death certificate, would get restricted. • See WebSurrogate December 2021 Upgrade Info, nycourts.gov; Hani Sarji, New York County Surrogate's Court Records Will Be Available on WebSurrogate Starting 11/6/2023, Wills, Trusts, Estates, Nov. 3, 2023.
Restricted Property Trust
"[A]n employer-sponsored plan that provides business continuity through a death benefit and potential long-term cash accumulation and income distribution" that was founded by Ken Crabb. Ken Crabb, Webinar: The Restricted Property Trust -- A Special Re-Broadcast, leimbergservices.com, July 20, 2023.
resulting trust
A trust that arises on the failure in whole or in part of an express trust.
retirement
"Retirement usually entails replacing your annual salary from a workplace with other sources to maintain your current lifestyle. Wile Social Security may cover part of your budget, . . . [t]he rest of your money will most likely need to come from your savings and investments." Emily Lorsch, Here's how much you need to save each month to earn $40,000, $50,000 and $60,000 per year in interest for retirement, CNBC, July 22, 2023 (Apple News link).
retirement plan fiduciary adviser
A fiduciary "responsible for managing the investments in a 401(k) or employer-sponsored retirement plan." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
retirement planning
"The core focus of retirement planning is on the accumulation of assets to live out one’s golden years. This includes regularly contributing to retirement accounts and investing those funds appropriately. Although this is unquestionably a crucial first step, an important second consideration that many investors neglect is ways to minimize expenses in retirement, which will allow one’s nest egg to last longer." Jonathan I. Shenkman, Retirees Have to Pay Taxes, Too. 6 Smart Ways to Reduce Them., Barron's, Nov. 22, 2023 (Apple News link).
Revenue Ruling 85-13
Provides that the transfer of assets between a grantor and a grantor trust is a non-taxable event for federal income tax purposes.
Revenue Ruling 2004-64
Holds that a gift tax does not apply to a grantor's payment of income tax attributable to trust income. • This holding effectively allows grantors to make additional, tax-free gifts to the trust beneficiaries.
reversion
A future interest in property that is retained when a transferor conveys a lesser estate than the transferor had. • A revision arises automatically by operation of law. • When a transfer is made by a will, the heirs of the transferor-testator retain the reversion because they are substituted by law for the decedent.
revolving debt
"Revolving debt is debt that is open-ended, meaning you can reuse it once you pay down your balance, as with a credit card. . . . [Y]ou get a maximum credit line and then you can spend up to that limit as many times as you need to. The available credit you have will fluctuate depending on how much credit you’ve used. With this type of debt, you must make at least the minimum payment, and the remaining balance will then transfer over to the next month with interest. " Investopedia, Debt: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link). C.f. installment debt.
risk management
"[R]isk management is just wealth management through another lens." Joel Schoenmeyer, Early Takeaways from SVB (Post 2), LinkedIn, March 15, 2023.
risk premium
"[T]he investor who bears the greater risk is compensated for it." John H. Langbein, The Uniform Prudent Investor Act and the Future of Trust Investing, 81 Iowa L. Rev. 641, 647 (1996).
risk-return curve
"[T]he obvious truth [is] that some securities are riskier than others. Investors demand to be paid to bear the greater risk. For example, a start-up computer software company in Silicon Valley entails a far larger risk of disappointing returns or total failure than does a seasoned blue chip such as Mobil Oil or General Electric. If you are a Silicon Valley entrepreneur who wants me to invest in your start-up firm, you must offer me an expected return (that is, a combination of dividends and capital appreciation on the securities) that is higher than Mobil or GE will pay me in order to induce me to invest in your riskier venture. This calculation is called the risk/return curve: The higher expected return on the investment compensates me for bearing the greater risk of the investment being disappointing." John H. Langbein, The Uniform Prudent Investor Act and the Future of Trust Investing, 81 Iowa L. Rev. 641, 647 (1996).
risk-tolerance surveys
Tools that financial advisors use to determine a client's tolerance for risk and assign labels, such as, "highly conservative" or "moderately aggressive." Some advisors use tools like Riskalyze, FinaMetrica, and DataPoints. Others are wary of such tools. See Morey Stettner, Risk-tolerance surveys often miss what financial advisers really need to know about you, MarketWatch, Feb. 2, 2023 (Apple News link).
robo adviser
"Robo-advisers use computer algorithms to create and manage an investment portfolio on a client's goals for a minimal fee. . . . [R]obo-advisers can make economical sense for someone with fewer assets." Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
rollover
For retirement: "A rollover happens when you pull money out of one plan and deposit it into another, which is different from a transfer that moves accounts between institutions." Kate Dore, These are the 3 biggest retirement plan rollover mistakes, expert says. Here's how to avoid penalties, CNBC, Sept. 29, 2023 (Apple News link).
Roth conversion
"Essentially, a Roth conversion entails transferring funds from traditional retirement accounts, which are subject to taxation upon withdrawal, to Roth IRAs. This strategic maneuver is aimed at eliminating future tax-related risks, reducing the overall tax burden over time and increasing the value of one's after-tax retirement savings." Troy Sharpe, Roth IRA Conversions: Benefits and Considerations Beyond Taxes, Kiplinger, Sept. 29, 2023 (Apple News link).
rule against perpetuities
The rule against perpetuities serves as a backstop to prevent dynasty trusts from eroding the estate and gift tax base. The common law rule against perpetuities is that an interest in trust is void unless it is certain to vest, if at all, no later than 21 years after the end of a “measuring life” (i.e., an identifiable person who is alive at the time the interest is created). See Hani Sarji, 🔑Even Under Common-Law Rule Against Perpetuities, Trusts Can Last for Over a Century, Wills, Trusts, Estates, Feb. 11, 2022.
Rule of 72
(1) "The Rule of 72 is an easy way to calculate how long it will take your investment to double in value. . . . You divide 72 by the annual rate of return you expect to earn on that investment. For example, if you expect an annual return of 8%, it would take approximately 9 years for your investment to double (72 divided by 8 equals 9)." Charles Lewis Sizemore, The Rule of 72 Is an Easy Way to Assess Your Investments. Are You using It?, Kiplinger, May 22, 2024 (Apple News link).
(2) "The Rule of 72 can also be used to assess the impact of inflation on your purchasing power. If you want to determine how long it will take for the purchasing power of your money to be cut in half due to inflation, you can use the same formula. Let's say the inflation rate is 3%. You could divide 72 by 3 to get 24 years. Assuming a 3% rate of inflation, your purchasing power would be cut in half in 24 years." Charles Lewis Sizemore, The Rule of 72 Is an Easy Way to Assess Your Investments. Are You using It?, Kiplinger, May 22, 2024 (Apple News link).• See the 📖Glossary book for additional details.
S
salary reduction contribution
See elective deferral contribution.
sanism
"[I]rrational prejudice against or judgment about persons with mental disabilities embodied in doctrine, policy, decisional application and other aspects of law." Pamela Champine, A Sanist Will?, Dec. 16, 2002 (SSRN link).
sans serif
See serif.
scoring a bill
An estimate of the economic impact of a tax bill. Scoring examines: (1) What a bill would cost taxpayers; (2) how much money will come out of the Federal Treasury; and (3) in the case of a tax bill, how much the bill would generate or reduce income to the Federal Treasury. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO), a non-partisan office, does the scoring. See Sen. Chuck Grassley, Ask Chuck: What does it mean to “score” a bill?, YouTube, Sept. 15, 2009.
scutage
In feudal times, in tenure by knight service, a monetary payment paid by a tenant to a lord (or tenants-in-chief to the king) in lieu of actually providing knights. Scutage became a form of direct tax, but it gradually fell into disuse as feudalism ended.
seal
(vb.) To prevent disclosure of documents, typically by a court order. See unseal order.
section 7520 interest rate
A rate that taxpayers use to calculate the present value of an annuity, an interest for life or for a term of years (including unitrust interests), a remainder, or a reversionary interest. The monthly rate is determined by multiplying the monthly Applicable Federal Midterm Rate by 120 percent and rounding the product to the nearest two-tenths of one percent. For example, the rate that is 120 percent of the applicable federal rate (compounded annually) for January 2023 is 4.62 percent. That rate is then rounded to the nearest two-tenths of one percent or 4.6 percent for purposes of IRC 7520. The section 7520 interest rate is published monthly by the Internal Revenue Service in the Internal Revenue Bulletin. See Reg. § 20.7520-1 (Valuation of annuities, unitrust interests, interests for life or term of years, and remainder or reversionary interests); Section 7520 Interest Rates, IRS.
secured debt
"[D]ebt backed by an asset used as collateral for amounts not paid. If the loan isn't paid back, the lender has the option to seize the asset." Investopedia, Debt: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link). C.f. unsecured debt.
seisin
In feudal times, the possession of land.
self-declared trust
A trust in which the grantor and the trustee are the same.
self-settled trust
A trust in which the grantor retains a beneficial interest (i.e., is a beneficiary).
separately managed account (SMA)
"[D]iscrete investment accounts held by individual investors for which the money is invested by a professional money manager. The account can begin as one of many investment-style templates available, but then are personalized by the money manager based on the financial and tax needs of the client, as well as the client’s individual preferences." Lori Ioannou, Brokerage Firms Are Pitching Separately Managed Accounts. Here's What to Know., WSJ, Jan. 7, 2024 (Apple News link). • SMAs also called "wrap accounts," "managed accounts," or "individually managed accounts."
serif
"A serif is not an angel (a seraph), but rather is a fine cross-stroke at the end of the principal stroke of a letter. Serifs enable the eye to move easily from letter to letter of a line of text and hence improve the readability of a document set in a serifed typeface. Sans serif typefaces lack serifs. Times Roman is a serifed typeface and Arial is a sans serif typeface. In the following examples, the serifs are the fine lines at the ends of the s, r, i, and f in the word serif, which is set in Times New Roman, and which are missing from the same letters in the words sans serif, which are set in Arial." Supreme Court of the State of New York, Appellate Division: Second Judicial Department, A Glossary of Terms for Formatting Computer-Generated Briefs, with Examples. C.f.* monospaced typeface.

The Appellate Division Second Department prohibits the use of a sans serif typeface: "The rules require the use of a serifed typeface to enhance the readability of the brief (22 NYCRR 1250.8[f][2]). The use of sans serif fonts is prohibited."
serjeanty tenure
In feudal times, land holding from a lord in exchange for a personal, non-military service to that lord. • "Serjeanty" is derived from the medieval Latin word, "serientia," which means "service." • The king's administrative and household officials (such as the marshal, steward, butler, and chamberlain) provided serjeanty tenure, a non-military service. See tenure. C.f. military tenure.
service
In feudal times, a duty, obligation, or monetary fee provided by a tenant to a lord. • The service was fixed at the creation of a tenure. • Some services were military in nature (see [military tenure](#military tenure)); others were non-military in nature (see serjeanty tenure).
service of process
The delivery of legal papers to the other party in a lawsuit, usually by personal delivery or mail.
settlement
An agreement between litigants about a case.
settlor
A person who creates a trust. Also called, "creator," "donor," "grantor," or "trustor."
short sale
See shorting a stock.
short-term capital gains
Capital gains on the sale of capital assets that are sold within one year of their purchase. Short-term capital gains are taxed at the tax rates for ordinary income. See capital gains.
shorting a stock
Betting that the price of a stock will decrease. • In a short sale, an investor sells borrowed shares, hoping to buy them back at a lower price. • See Joanna Tan, Elon Musk says he confronted Bill Gates about shorting Tesla, CNBC, April 23, 2022 (Apple News link).
silent trust
A trust that limits the information that beneficiaries receive about the trust.
Silicon Valley Bank
A California-based, regional bank serving U.S. venture capitalists and technology startups that rapidly collapsed in March 2023, which was the second-biggest bank failure in U.S. history in terms of assets, leading the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. to take control of the bank by creating a new entity, the Deposit Insurance National Bank of Santa Clara, which received all of SVB's deposits. The reason for SVB's collapse is because it purchased Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed bonds when interest rates were at historic lows, but these securities declined in value when interest rates rose. Instead of holding on to the bonds, as it intended, SVB was forced to face up to the losses when it was flooded with withdrawal requests in March 2023: Clients tried to withdraw $42 billion on March 9. See Rachel Louise Ensign, Corrie Driebusch & Meghan Bobrowsky, Silicon Valley Bank Closed by Regulators, FDIC Takes Control, WSJ, March 10, 2023 (Apple News link); Peter Santilli & James Benedict, Silicon Valley Bank's Meltdown Visualized, WSJ, March 11, 2023 (Apple News link).
skip person
For purposes of the generation-skipping transfer tax, a transferee who is two or more generations younger than the transferor. IRC § 2613. Examples: (1) In a transfer from grandparent to a grandchild, the grandchild is a skip person. (2) In a transfer from a great-uncle to a great-niece, the great-niece is a skip person.
slave
In feudal times a person who was the property of a lord and had no lands. C.f. freeman.
socage tenure
In feudalism, "the great residual tenure. A free tenant who did not hold by military service, serjeanty, or frankalmoin was deemed to hold in socage. . . . It was destined to become . . . the one surviving form of tenure." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 12 (7th ed. 2020).
sole proprietorship
A business enterprise that is owned and operated by a single individual who report the business's income and expenses on their individual tax return (Form 1040) by filing the appropriate schedule -- Schedule C (sole proprietorship generally), Schedule E (rental real estate and royalties), and Schedule F (farms).
Sotheyb's
The auction house owned by French telecom billionaire Patrick Drahi.
sovereign wealth fund
"[S]overeign wealth funds invest national surpluses, often derived from oil, natural resources, or government-controlled assets. They can fund infrastructure projects, public services, or direct payments to citizens. Alaska’s $80 billion fund, for example, pays annual dividends to residents, distributing over $900 million in 2024." The Wealth Advisor, Trump's Executive Order For A US Sovereign Wealth Fund: What Could That Mean, Feb. 5, 2025.
special guardian
See guardian ad litem.
special needs trust
"This article refers to 'supplemental needs trusts' or 'special needs trusts' interchangeably. Both terms broadly describe a trust designed to benefit a person with a disability (the beneficiary) without jeopardizing the beneficiary’s eligibility for public benefits." Mark Brody & Sheila Shea, Birth of a Third Party Agency Trust, NYSBA Elder and Special Needs Law Journal, Fall 2019.
special verdict
A verdict by which the jury resolves specific fact questions, which are submitted to them by the judge.
spendthrift clause
A clause in a trust that protects a beneficiary's interest from the claims of creditors.
SPLAT
An acronym that stands for spousal access lifetime trust.
sprinkle trust
A trust that gives the trustee has the discretion to distribute income among specified persons. The trustee determines whether and to what extent to distribute trust income. A sprinkle trust is used in lieu of separate trusts for each beneficiary.
squeaky wheel principle
The idea that the loudest problem is the one that gets the most attention. See The squeaky wheel gets the grease, Wikipedia. • Example demonstrating the squeaky wheel principle: On August 22, 2023, a lawyer posted the following on the New York State Bar Association's Trusts and Estates Law Section: "I found that you have to go into the Kings County [Surrogate's Court] court frequently to ask about the file. On one occasion they lost the original will and the court just stopped working on the file. We had to prod them into proceeding. On another occasion, the file was ready to go but was found sitting in a cabinet. Once they took it out of the cabinet, I got letters in 2 weeks. They seem to discover things when you ask about the file. In person is best."
stagflation
Periods of high prices and slow growth.
standard deduction
A set amount that taxpayers subtract from taxable income if they do not list (i.e., itemize) their deductions on Schedule A (Form 1040). • "The amount of the standard deduction depends on the taxpayer's filing status, age, and whether they are blind or a dependent of another taxpayer." Robert Powell, Reduce Your Tax Bill With These Deduction Strategies, TheStreet, July 31, 2023 (Apple News link).
state and local tax (SALT) deduction
"SALT . . . allows taxpayers who itemize to deduct certain state and local taxes against federal taxes paid. The 2017 tax overhaul instituted a $10,000 limit on that deduction, slated to run through 2025. On Capitol Hill, a fight is brewing over whether to increase the amount that can be deducted beyond $10,000." John Tamny, Opinion: Why Lawmakers Should Pass the SALT Deduction, WSJ, Aug. 15, 2023 (Apple News link).
static 529 plan
"Static plans allow investors to be more involved and find a plan that aligns with their respective risk level." Keith Reid-Cleveland & Patricia Oey, What Is a 529 College Savings Plan?, Morningstar, Nov. 2, 2022 (Apple News link). C.f. age-based 529 plan.
status quo bias
Preference for the current state of affairs.
Statute of Frauds
A rule that invalidates oral agreements respecting real property. • Example from Michigan: Laura Morris, Are Oral Instructions for Real Estate Transfers Enforceable in Probate Court?, JD Supra, June 28, 2023: "No, it is not enforceable according to In re Estate of Finney, Docket No 361305 (Mich Ct App June 15, 2023) (unpublished). . . . While most oral agreements are enforceable, the statute of frauds requires agreements regarding real estate to be in writing. MCL 566.106." • Example from New York: "The alleged oral agreement is one for an interest in real property and thus falls within the purview of the Statute of Frauds which holds that '[a]n oral agreement to convey an estate or interest in real property, other than a lease for a term not exceeding on year, is nugatory and unenforceable,' and '[a] party to the agreement may legally and rightfully refuse to recognize or perform it' (*Woolley v Stewart, 222 NY 347, 350-351; see, General Obligations Law § 5-703)." Pattelli v. Bell, 187 Misc.2d 275, 721 N.Y.S.2d 734 (Supreme Ct., Richmond Co. 2001). • C.f. part performance.
Statute of Wills (1540)
A law in England that allowed land to be devised. • Prior to the Statute of Wills, land descended to the eldest son, and landowners who wanted to deviate from primogeniture turned to uses.
Statute Quia Emptores (1290)
(1) "[G]ranted to 'every freeman'' the right to alienate without paying a fine to his lord. This statute was construed as not affecting the rights of the king, such that tenants in capite continued to be subject to fines for alienation until 1660, with the adoption of legislation abrogating most of the incidents of tenure." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 18 (7th ed. 2020).
(2) Prohibited the grant of land in frankalmoin by anyone other than the king, unless they obtained the king's permission.
statutory buyout
For an LLC: "[W]here one member sues for dissolution, the other members can trigger a statutory right to purchase the plaintiff members interest . . . ." Kevin Brodehl, "Equitable Buyout" as a Remedy for LLC Wrongdoing?, JD Supra, June 26, 2023. See California Code, Corporations Code § 17707.03(c). C.f. contractual buyout, equitable buyout.
statutory will
Another term for the laws of intestacy (or laws of descent and distribution). • Each state has enacted statutes that provide a default distribution scheme (i.e., a default estate plan) that approximates the disposition of assets that a typical person would make upon death.
stipulated facts
A statement of facts that litigants agree upon. Stipulated facts streamline the litigation because the litigants do not have to prove those facts. If litigants agree to all of the facts, then the issue is about the law that governs the legal questions raised by the facts or the application of the law to the facts.
"still working" exception for RMDs
"The 'still working' exception allows RMDs to be delayed for a retirement plan from an employer for whom someone is still employed. Therefore, this doesn’t apply to an old 401(k) at previous employers. Nor does it apply to IRAs, SEPs, and SIMPLE IRAs. When you use the 'still working' exception, RMDs begin in the year you separate from service. Your required date to begin taking RMDs will be April 1 of the year after separation from service. // The definition of 'still working' has no official specifics from the IRS. Consequently, working part time may be sufficient to take advantage of this strategy. It’s important to note that you can’t use the exception if you own more than 5% of the company for which you are still working." Jonathan I. Shenkman, Retirees Have to Pay Taxes, Too. 6 Smart Ways to Reduce Them., Barron's, Nov. 22, 2023 (Apple News link).
stock buyback
When a public company repurchases its own stock. • A stock buyback can increase the stock's price and increase earnings-per-share. • Proponents of stock buybacks argue that they benefit all owners of the company; opponents of stock buybacks argue that stock buybacks are a form of market manipulation ("nothing but paper manipulation," decries Elizabeth Warren), cannibalize innovation, and misuse capital (capital is used to push stock prices up rather than for a capital expenditure, such as a new factory, or dividends). See Will Daniel, Tactic Facilitates 'Stock Manipulation' and Hurts the Economy, Wealth Advisor, April 11, 2023.
subject to
In law, when something is "subject to" a particular condition, it means that the occurrence or non-occurrence of that condition will affect the validity or enforceability of a legal obligation or agreement. For example, if a contract is subject to a condition precedent, the contract will only become binding and enforceable if and when that condition is met. Similarly, if a person receives an inheritance subject to certain restrictions or conditions, their rights to the inheritance may be affected by their compliance with those restrictions or conditions. In short, the phrase "subject to" is often used in legal contexts to indicate that a particular obligation, right, or benefit is conditional upon the occurrence of a specified event or condition.
subpoena ad testificandum
An order to a witness to appear in court and give testimony.
subpoena duces tecum
An order to a subpoenaed party to appear in court and bring specified documents. • "A subpoena duces tecum for use at a hearing is not the equivalent of an order of disclosure, but an order to the subpoenaed party to have the documents in court so that the court may make appropriate direction with respect to the use of such documents. People ex rel. Hickox v. Hickox, 64 AD2d 412, 413-14 (1st Dept. 1978)." Harbor Tech LLC v. Correa, 73 Misc.3s 1211(A), 2021 N.Y.Slip Op. 50995(U) (Kings Co. Civil Court Oct. 14, 2020, Stoller, J.).
successor agent
In a power of attorney: One or more people whom the principal can designate who will serve as the agent in the event any initial or predecessor agent resigns, dies, becomes incapacitated, is not qualified to serve, or declines to serve. NY GOL 5-1508(2).
successor trustee
Someone who can take over as trustee and manage the trust's assets when the acting trustee dies, becomes incapacitated, resigns, or is removed.
sundowner’s syndrome
"[A] state of confusion occurring later in the afternoon and night often found in individuals with dementia or Alzheimer’s." Kelly Mould, Opinion: Cognitive Decline: how to spot it, what to do, MarketWatch, Jan. 21, 2023 (Apple News link).
supplemental needs trust
See special needs trust.
supported decision making
An informal arrangement or written agreement ("Supported Decision Making Agreement") that allows adults with disability to retain their automony and make their own decisions, albeit with support. • In Bill No. 1663, passed on January 1, 2023, California passed SDM legislation, but it has shortcomings that need to be worked out: "[S]hould the SDM be compensated; are third parties, such as doctors or banks, required to accept the decision maker’s decision; and the big one, is the decision maker held to a fiduciary standard?" Liza Horvath, An alternative to conservators, Monterey Herald, July 1, 2023.
surcharge
An order or decree of a court that imposes liability on a fiduciary upon a successful exception to the fiduciary's cash or property account.
surrender and admittance
In feudal England, land held in copyhold tenure could be transferred only by surrender and admittance, rather than the common-law methods of feoffment and grant that were available to tenants hold by free tenure. The copyhold tenant could, by custom, surrender the land to the lord of the manor and designate another person as the tenant; and the lord was bound to admit this person into the tenancy. See villein.
surviving executor
The executor where there are two or more executors, and one or more die.
T
target-date fund
A mutual fund that gradually adjusts asset allocation over time into more conservative categories as it approaches a target retirement age. • "[A] diversified target-date fund . . . shifts money from stocks to bonds as investors age . . . ." Anne Tergesen, Why a Bull Market Is a Bad Time to Check Your 401(k), WSJ, June 15, 2023 (Apple News link).
tarrif
"Here’s the short answer: Tariffs are a tax on imported goods. They generally make affected consumer products more expensive. In theory, well-designed tariffs will also encourage targeted industries to produce more in the United States. And manufacturing certain goods domestically — instead of importing them from abroad —may have national security or economic benefits. Trump’s own rationales for his tariffs are numerous and shifting: He sees them as a tool for raising revenue, enhancing national security, and revitalizing the US economy by increasing domestic manufacturing jobs. But the president’s tariffs are so broad, high, and ever-changing that they could actually backfire." Eric Levitz, 5 big questions about Trump’s tariffs and how they might work, Vox, April 2, 2025 (Apple News link).
tax accounting
For trusts: Tax accounting is the process of preparing and filing tax returns for the trust and its beneficiaries. Tax accounting follows the rules and regulations of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the state tax authorities. Tax accounting is mainly concerned with complying with the tax laws and minimizing the tax burden of the trust and its beneficiaries. C.f. fiduciary accounting.
tax advisory services
Services that "go beyond the tax return and into the world of tax strategy and optimization." What is tax advisory?, Thomson Reuters, July 6, 2023. C.f. tax compliance services.
tax bracket system
"The U.S. and many countries use . . . a tax bracket system in which a different tax rate is applied to different levels of taxable income." TheStreet Staff, What Is a Marginal Tax Rate? Definition & Example, TheStreet, May 24, 2023 (Apple News link).
tax cliff
Regarding an estate tax: Having an estate tax exemption apply and then having it immediately and completely disappear at the next dollar. • "It is important to reiterate that no tax is due on estates whose Connecticut taxable estate is $2 million or less. However, where the Connecticut taxable estate exceeds the $2 million threshold, the basis for the tax is the total value of the Connecticut taxable estate, including the first $2 million. This is known as the 'cliff' effect. You will see references to the cliff in our survey responses." Estate Tax Study, Connecticut Department of Revenue Service, Feb. 1, 2008.
tax compliance services
Services that include preparing federal, state, and local tax returns. C.f. tax advisory services.
tax credit
Reduces taxes dollar-for-dollar.
Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA)
A major tax reform law that was passed in 2017. It lowered the tax rates for individuals and businesses, increased the standard deduction and the estate tax exemption, and made other changes to the tax code. However, most of the changes for individuals are not permanent and are set to expire by the end of 2025, unless Congress extends them or enacts new legislation. This means that starting from 2026, the tax rates and brackets will revert to their pre-TCJA levels, the standard deduction will decrease, and the estate tax exemption will be halved.
tax deduction
Reduces taxable income.
tax installment agreement
A long-term monthly payment plan through the IRS. If you owe $50,000 or less for tax, penalties, and interest; then you can set up an installment plan online. For larger amounts, you must call the IRS.
taxable income
Adjusted gross income minus the greater of the standard deduction or itemized deductions. • When computing income taxes, taxpayers apply income tax rates to taxable income.
tax-loss harvesting
A tax strategy that uses losses to offset profits. See Kevin Khang, Thomas Paradise & Joel M. Dickson, Tax-loss harvesting: A portfolio and wealth planning perspective, Vanguard, Oct. 2020; Greg Iacurci, As stocks tumble, this tax play offers a silver lining, CNBC, May 9, 2022 (Apple News link); Kate Dore, Here's when tax-loss harvesting makes sense . . . and when it doesn't, CNBC, June 8, 2022 (Apple News link); Laura Saunders, Got Losses on Stocks, Bonds or Crypto? There's a Silver Lining at Tax Time, WSJ, June 10, 2022 (Apple News link). • "Tax-loss harvesting is one reason many people are opening SMAs for direct indexing—an investment strategy that involves buying the underlying securities of an index such as the S&P 500. It lets them sell individual stocks that have declined in value to realize losses so they can offset capital gains and to keep more profits." Lori Ioannou, Brokerage Firms Are Pitching Separately Managed Accounts. Here's What to Know., WSJ, Jan. 7, 2024 (Apple News link).
tax planning
Creating and implementing a plan to minimize taxes. • Tax preparation is essentially forward-looking. C.f. tax preparation.
tax preparation
Reporting income and deductions on a tax return. • Tax preparation is essentially backward-looking. C.f. tax planning.
tax rate
The percent by which a tax base is multiplied to determine a taxpayer's tax liability. See, e.g., IRC §§ 1 (federal income tax), 2001 (federal estate and gift taxes), 3101 (federal employment tax), and 4001 (federal excise taxes).
tenancy by the entirety
A special joint ownership for married couples based on the idea that a married couple is one person. Each spouse owns the whole, not a share of the whole. Creating it requires the four unities of time, title, interest, and possession. Its key feature is a right of survivorship, which is indestructible. This means that upon the first spouses' death, the surviving spouse remains seized of the entire property. The right of survivorship is indestructible because a spouse cannot bring a partition action to sever and terminate the tenancy by entirety, and one spouse cannot defeat the other spouse's right of survivorship. • In New York, a tenancy by the entirety applies only to real property and COOPs. EPTL 6-2.1(4). It is the default estate when such property is transferred to a married couple. EPLT 6-2.2(b), (c). The deed does not need to recite the intent or interests of the parties. See Bartholomew v. Marshall, 257 A.D. 1060, 13 N.Y.S.2d 568 (3rd Dep't 1939) (where property was conveyed to husband, wife, and child "without further words showing the intention of the parties," finding that "[w]hen real property is conveyed to a husband and wife and third person, the husband and wife have one moiety as tenants by the entirety, and the third person is a tenant in common with them of the other."). • The notion of two people, each owning the whole individual, as if they were one person is difficult to grasp and counterintuitive. In a dissenting opinion, Chief Justice Weintraub stated, "The estate by entirety is a remnant of other times. It rests upon the fiction of a oneness of husband and wife. Neither owns a separate distinct interest in fee; rather each and both as an entity own the entire interest. Neither takes anything by survivorship; there is nothing to pass because the survivor always had the entirety. To me the conception is quite incomprehensible." King v. Greene, 30 N.J. 395, 413, 153 A.2d 49, 60 (1959). • A tenancy by the entirety "is incompatible with community property system's basic theory of a conjugal partnership in acquisitions and gains and, therefore, was never recognized in the eight community property states." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 303 (7th ed. 2020).
tenancy in partnership
"[A]s the name indicates, a unique form of co-ownership by which specific partnership assets, both real and personal, are held by partners. The concept of tenancy in partnership is a creation of the Unif. Partnership Act, § 25. The Act has been adopted in all states. See 6 U.L.A. 7 (Supp.1987)." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 309 n.1 (7th ed. 2020).
tenant in capite
See tenant-in-chief.
tenant-in-chief
In feudal times a person holding land directly under the king. In Latin, the term is "tenant in capite."
tenant in demesne
In feudalism, an individual who actually occupied land and "had property rights consisting of a general right to possess, use, and enjoy the land." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 7 (7th ed. 2020).
tenants paravail
In feudalism, peasants who tilled the soil. Tenants paravail formed the broad base of the pyramidal feudal social structure.
tenure
In feudal times land holding from a lord in exchange for a service to that lord. • Tenure was classified either as unfree or free.
tenure by divine service
In feudalism, a type of frankalmoin tenure that required specific religious acts (such as saying mass for the grantor a specific number of times a year) by the religious grantee.
tenure by knight service
See military tenure.
term
For a bond: "[T]he amount of time over which it is scheduled to make payments." Penelope Wang, 8 Things You Need to Know About Bonds, AARP Bulletin, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link).
testament
Traditionally, an instrument disposing personal property. • Historically, a testament related solely to personal property and a will to real estate. • C.f. will.
testamentary substitutes
Ways of passing property at death other than a will. • Testamentary substitutes include lifetime trusts, joint ownership with a right of survivorship, and assets that have a beneficiary designation filled out (such as life insurance and retirement plan designations).
testamentary trust
A trust that is created under a will and takes effect after the testator dies. C.f. lifetime trust.
testate
Someone who dies with a will. C.f. intestate.
testator
Someone who writes a will
the 4% rule
"Once you have an idea of what your annual spend will look like, you can work backwards using the 4% rule, which essentially says that you can safely withdraw 4% of your retirement assets each year." Laila Maidan & Kathleen Elkins, FIRE Movement: Early retirees discuss limitation, need to resume working, Business Insider, Sept. 13, 2023 (Apple News link).
the fiduciary obligation
See fiduciary duty.
the great wealth transfer
"[W]hen Baby Boomers will pass on more than $70 trillion in wealth to younger generations." Allison L. Lee, I Wish I May, I Wish I Might: Estate Planning's Gentle Nudge, Kiplinger, March 22, 2023 (Apple News link). • Cerulli Anticipates $84 Trillion in Wealth Transfers Through 2045, Cerulli Associates, Jan. 20, 2022.
The New Domesday Book
A survey of Great Britain conducted in 1874. • See Domesday Book.
the observer effect
“[T]he fact that observing a situation or phenomenon necessarily changes it,” Ken Baclawski, The Observer Effect.
the TINA effect for stocks
A market in which bond yields are so low that stocks are the only investment choice. • "Tina" stands for "there is no alternative." Investing in just stocks instead of allocating funds between stocks and bonds is considered suboptimal. See Investopedia, TINA: There Is No Alternative. • For example, the "TINA effect" occurred in August 2019 when 60% of the stocks in the S&P 500 (1.7%) and most individual sectors offered dividend yields that exceeded the yield on 10-year U.S Treasury notes (1.640%). See Michael Wursthorn, Falling Bond Yields Make Equities Hard to Ignore, WSJ, Aug. 13, 2019 (Apple News link). • In April 2022, market conditions (falling stock prices and rising bond yields) signaled the end of the TINA effect. See Dion Rabouin, Wall Street Finds New Value in Cash as Global Fears Weigh on Markets, WSJ, April 25, 2022 (Apple News link).
Thrift Savings Plan (TSP)
A retirement plan for employees of the United States government, including members of the uniformed services. See https://www.tsp.gov/
time value of money
"Money received sooner is more valuable than money received later. . . . Present-value calculations overcome the initial objection to breakeven analysis by accounting for the time value of money. Payments received this year are treated as being more valuable than those received the next year, and so forth." John Rekenthaler, Should You Delay Taking Social Security Benefits?, Morningstar, Sept. 28, 2023 (Apple News link).
title
Respecting real property: "The word 'title' has two meanings: 1) the right to ownership of real property, and 2) evidence of ownership by a deed." Terrence Dunn & Ira H. Goldfarb, Title to Real Property, New York City Bar: Legal Referral Service, July 2017. • "A properly-conveyed deed should be recorded to provide notice to the world of ownership. Title to real property can be held by one person or by multiple people. Title can also be held by a trust or a business entity. When title is held by more than one owner, there are three ways to hold title to the same property: Tenants in common . . . Joint tenants . . . Tenants by the entirety . . . ." Id.
title insurance
Insurance that protects owners of real property and mortgage lenders against future claims for past defects in a chain of title regarding a specific piece of property. • Title insurance covers defects in a property's title that show up on a title report, such as an open mortgage, a governmental lien, or an open mortgage. • Title insurance does not cover (1) the value of the property (so, it doesn't insure that someone is getting a good deal for the purchase price), (2) the use of the property (e.g., commercial or residential), (3) the zoning of the property (e.g., high density zoning v. low density zoning), (4) the ability to obtain permits from municipalities, (5) hazardous materials (i.e., environmental issues), and (6) issues regarding the land (e.g., damage caused by activities on adjacent properties).
title report
A written analysis of the status of title to real property.
tokens
See coins.
total return
(1) Investment: "Total returns 'include dividend reinvestment as well as price appreciation.' R. Ibbotson, G. Brinson, Investment Markets 65 (1987)." Joel C. Dobris, Probate World at the End of the Century: Is a New Principal and Income Act in Your Future, 48 Rec. Ass'n B. City N.Y. 280 (1993).
(2) Trust investment: A trust investment approach that strives for "the optimal amount of gain for the trust given its risk/reward tolerance, regardless of whether the gain is classified for trust accounting purposes as income or principal. Although this investment approach may maximize the financial success of the trust as a whole, it exacerbates the conflict between the income beneficiaries and the remaindermen, who have strong preferences about whether the character of the receipt from the investment lands in the 'income' account or the 'principal' account." Alyssa A. DiRusso & Kathleen M. Sablone, Statutory Techniques for Balancing the Financial Interests of Trust Beneficiaries, University of San Francisco Law Review, Winter 2005.
total return swap
"We may enter into a total return swap ('TRS') agreement. A TRS is a contract in which one party agrees to make periodic payments to another party based on the change in the market value of the assets underlying the TRS, which may include a specified security, basket of securities or securities indices during a specified period, in return for periodic payments based on a fixed or variable interest rate. A TRS effectively adds leverage to a portfolio by providing investment exposure to a security or market without owning or taking physical custody of such security or investing directly in such market. Because of the unique structure of a TRS, a TRS often offers lower financing costs than are offered through more traditional borrowing arrangements. We would typically have to post collateral to cover this potential obligation." HPS Corporate Lending Fund, Form 10-K, March 21, 2024.
total return trust (TRT)
"Without the ability to adjust the amount that can be distributed to the income beneficiary, Total Return investing is a moot point. A 'Total Return Trust,' then, is a trust that (by trust instrument, law or fiduciary discretion) allows the fiduciary to invest for Total Return but also allows adjustment of the amount to be distributed to the current beneficiary, without regard to whether the distribution is composed of dividends, interest, rent, capital gain or otherwise. We do not, however, restrict the term 'Total Return Trusts' to only those trusts that can distribute fiduciary accounting 'income.' We include in the definition all trusts that allow for discretionary distributions of income and principal, since the practical result of making a discretionary distribution versus changing the definition of income are essentially the same is a trust that (by trust instrument, law or fiduciary discretion) allows the fiduciary to invest for Total Return but also allows adjustment of the amount to be distributed to the current beneficiary, without regard to whether the distribution is composed of dividends, interest, rent, capital gain or otherwise." Paul S. Lee, Implementing Total Return Trusts (2002). See total return.
total value locked
"[M]easures assets deposited as collateral on DeFi platforms." Paul Vigna, DeFi Is Helping to Fuel the Crypto Market Boom -- and Its Recent Volatility, WSJ, June 3, 2021 (Apple News link). See decentralized finance.
Totten trust
From footnote 26 of the Third Report of the Temporary State Commission on the Modernization and Simplification of the Law of Estates to the Governor and the Legislature, May 31, 1964: "So called because In the Matter of Totten, 179 N. Y. 112, 71 N. E. 748 (1904), established the place in New York of the informal revocable trust of a savings-bank deposit. The Court of Appeals therein announced the following conclusion: 'A deposit by one person of his own money, in his own name as trustee for another, standing alone, does not establish an irrevocable trust during the lifetime of the depositor. It is a tentative trust merely, revocable at will, until the depositor dies or completes the gift in his lifetime by some unequivocal act or declaration, such as delivery of the passbook or notice to the beneficiary. In case the depositor dies before the beneficiary without revocation, or some decisive act or declaration of disaffirmance, the presumption arises that an absolute trust was created as to the balance on hand at the death of the depositor.' Id. at 125-26, 71 N. E. at 752."
Treasuries
See U.S. Treasuries.
Treasury inflation-protected securities (TIPS)
"[A] type of Treasury bond whose principal is indexed to inflation and used to protect investors from inflation . . . ." Lisa Scherzer, Bonds Are a Great Buy Now. How to Protect Yourself., Barron's, Aug. 19, 2023 (Apple News link).
treasury shares
See treasury stock.
treasury stock
Refers to shares that were once outstanding and have been bought back by the issuing company from shareholders. These shares are then held by the company, reducing the total number of shares available on the open market. • Also known as treasury shares or reacquired stock.
trial by judge
See bench trial.
trust
A legal device in which a settlor transfers the legal title of assets to one or more trustees, who manage and distribute the assets to one or more beneficiaries. • A property owner uses a trust in lieu of making an outright gift. • A trust makes it "possible to separate the benefits of ownership from the burdens of ownership." 1 Austin W. Scott, Trusts §1, at 2 (William F. Fratcher 4th ed. 1987), qtd in Jesse Dukeminier et. al., Wills, Trusts, and Estates 771 (7th ed. 2005). • "[T]he modern trust is preeminently a management device for separating ownership and enjoyment . . . ." John H. Langbein, The Contractarian Basis of the Law of Trusts, 105 Yale L.J. 625 (1995). • "[T]he normal private trust is essentially a gift, projected on the plane of time and so subjected to a management regime." Bernard Rudden in 44 Mod. L. Rev. 610 (1981) (book review), qtd in Jesse Dukeminier et. al., Wills, Trusts, and Estates 771 (7th ed. 2005). • See the 📖Glossary book for additional details.
trust fiduciary law
"Trust fiduciary law regulates the trustee's exercise of discretion. Be it in trust law or in other fields of fiduciary obligation (for example, corporations, agency, or partnership), fiduciary duties are default norms imposed in juridical relations that feature 'scope for the exercise of discretion.'" John H. Langbein, The Contractarian Basis of the Law of Trusts, 105 Yale L.J. 625 (1995). See fiduciary duty.
trust protector
One or more people named in a trust to act in a non-fiduciary capacity to ensure the trustee is adhering to the trust settlor’s intent and wishes.
trustee
"Trustees are the legal owners of the trust. As such, they control the management of the trust assets and the distributions a beneficiary receives. The trustee cannot use the trust assets for their benefit, but they have to act honestly and in good faith for the benefit of the beneficiaries and abide by the trust terms." Christine Fletcher, Unhappy With Your Trustee? 5 Ways To Remove Or Replace A Trustee, Forbes, Dec. 22, 2023 (Apple News link). • In a third-party trust, a person (i.e., an individual or a financial institution) who accepts the transfer of assets from a settlor and agrees to manage and distribute the assets to the trust's beneficiaries pursuant to the terms of the trust agreement. In a trust where the settlor is the sole trustee, an individual who makes a written declaration to manage and distribute assets (that the individual transferred to the trust) to the trust's beneficiaries (who the individual named). • Trustees are fiduciaries, which means they are held to a higher standard when discharging their duties. • A trust can name one or more trustee. • When a trust has more than one trustee, the trust should state whether they have the same or different duties, and whether they can act jointly or separately.
trustor
See settlor.
turnkey property
"Turnkey properties are homes that are fully functioning and ready to rent out immediately." Kathleen Elkins, How to use HELOC home equity line of credit buy property build wealth, Business Insider, Oct. 13, 2022 (Apple News link).
typeface
"[A] complete set of characters of a particular and consistent design for the composition of text, and is also called a font. Typefaces often come in sets which usually include a bold and an italic version in addition to the basic design." Supreme Court of the State of New York, Appellate Division: Second Judicial Department, A Glossary of Terms for Formatting Computer-Generated Briefs, with Examples.
U
ultra-high-net-worth individuals (ultra-HNWI)
A category of high-net-worth individuals "with $30 million or more" in investible assets. Quentin Fottrell, 'We've never seen this before': Millionaires are doing something unusal to preserve their wealth -- and you can do the same, MarketWatch, June 28, 2023 (Apple News link). • C.f. midtier millionaires and "millionaires next door".
ultrashort bond strategy
"[I]nvests in zero- to one-year high-quality corporate bonds, asset backed securities and the like . . . ." Lisa Scherzer, How to Move Out of Cash Before Interest Rates Drop, Barron's, June 29, 2024 (Apple News link).
underscore
(1) Literal meaning: To draw a line under a word to emphasize it.
(2) Figurative use: To emphasize the importance of something. Example: "The APA’s history and the contemporaneous views of various respected commentators underscore the plain meaning of its text." Loper Bright Enterprises et al. v. Raimondo, Sec’y of Commerce, et al., 603 U. S. ____ (2024).
undervalued investment
An asset that is worth more than what it costs.
undue influence
In a will contest: "[S]omeone claims you only made the will because you were in a weakened mental state and you were influenced by someone stronger to divide your property in a way that goes against your wishes." Will Contests, New York City Bar Legal Referral Service.
unfree tenure
In feudalism, tenure where the services depended on the will on the lord and were of a servile nature. • Unfree tenants could assert legal remedies against those disturbing their possession only in each tenant's lord's court (not in the king's courts). C.f. free tenure.
unhosted wallet
"Other owners [of digital assets] do not use the services of a hosted wallet provider and instead store private keys in a software program or written record, often referred to as an unhosted wallet. In general, only the user of an unhosted wallet has access to both the public and private keys necessary to effect transactions in the digital assets associated with those keys. Additionally, some providers of unhosted wallets also provide their unhosted wallet users with online platform services, which may include links or other mechanisms for direct access to third party services that allow users to buy and sell digital assets held in their unhosted wallets." Gross Proceeds and Basis Reporting by Brokers and Determination of Amount Realized and Basis for Digital Asset Transactions, Proposed Rule by the IRS, Aug. 2023. See digital asset account and digital assets. C.f. hosted wallet.
Uniform Fiduciary Income and Principal Act (UFIPA)
"The Uniform Fiduciary Income and Principal Act (UFIPA) is a revision of the former Uniform Principal and Income Act with a new name to differentiate the act from its three predecessor versions. While older trusts often had clear delineation between income and principal interests, modern trust accounting requires flexibility. Trustees now tend to invest for the greatest total return, and then adjust between interest and principal to produce a fair result for all the beneficiaries. UFIPA recognizes this trend toward total-return investing and includes unitrust conversion rules to allow even older trusts to take advantage of modern investment trends. UFIPA gives estate planning attorneys additional flexibility to tailor a trust for each client’s needs and includes a new governing law section to help avoid jurisdictional disputes." Fiduciary Income and Principal Act, ULC.
Uniform Management of Institutional Funds Act (UMIFA)
"Simplifying, UMIFA, or the Uniform Management of Institutional Funds Act, is the act that freed, but did not force, nonprofits to invest endowments for total return, rather than for income, and freed them to allocate returns as they saw fit. They could allocate to current needs or to endowment principal. Under UMIFA nonprofits can invest endowment as they wish and can allocate as they wish. UMIFA solves problems similar to those we face in investing the principal and allocating the income from private trusts." Joel C. Dobris, Probate World at the End of the Century: Is a New Principal and Income Act in Your Future, 48 Rec. Ass'n B. City N.Y. 280 (1993) (citations omitted).
Uniform Principal and Income Act (UPIA)
"The Uniform Principal and Income Act (UPIA) was originally adopted in 1931 at the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws. The UPIA has been amended several times over the years. Generally, the UPIA provides rules to determine who’s entitled to property, income and principal in a trust or estate and how receipts and disbursements should be allocated between principal and income." Francine Lee, The Nuts and Bolts of Fiduciary Accountings, Trusts & Estates, May 2021.
unitary executive theory
"[M]any conservatives contend that federal agencies and the Congress that authorized them have assumed too much authority. They espouse what is known as 'unitary executive theory.' It holds that a president should have virtually unlimited control over federal agencies and personnel, regardless of how much independence Congress may attempt to give them." Gerald F. Seib, Will the Other Two Branches Dare to Push Back Against Trump?, WSJ, Feb. 7, 2025 (Apple New link).
unitrust
"[A] trust where no distinction is drawn between income and principal and a set percentage of asset value is paid out annually in lieu of income." Joel C. Dobris, Probate World at the End of the Century: Is a New Principal and Income Act in Your Future, 48 Rec. Ass'n B. City N.Y. 280 (1993). • "In a unitrust the payout to the income beneficiary is a fixed percentage of the fair market value of the trust as revalued each year." Matter of Ives, 192 Misc. 2d 479 (NY Sur. Ct., Broome Co. 2002).
unrealized gain
An asset that has appreciated in value but has yet to be sold.
unrealized gains tax
"A tax on unrealized gains would mean that even if you had not sold a stock or other asset, you would need to pay tax on it if it appreciated in value." Zain Jaffer, *Unrealized Gains Should Not Be Taxed, Kiplinger, July 17, 2024 (Apple News link) ("In March, President Joe Biden announced a plan to raise revenues for the U.S. government by taxing unrealized gains on assets for those claiming over $100 million in assets. . . . While I'm not an economist, as an investor who runs a family office, I believe that instead of taxing unrealized gains, what the government really ought to do is to rein in its spending.").
unrealized loss
An asset that has gone down in value but has yet to be sold.
unseal order
A court order that permits the disclosure of sealed documents, such as search warrants. See seal.
unsecured debt
Debt that does not require collateral. "When a lender makes a loan with no asset held as collateral, it relies on the borrower's ability to repay the loan." Investopedia, Debt: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly, Aug. 2023 (Apple News link). C.f. secured debt.
upstate New York
"Upstate New York has been defined as north of Sullivan, Ulster, and Dutchess Counties and parts of Greene and Columbia Counties (upstate). Report from Real Property Section Committee on Professionalism Concerning Executive Committee’s Survey of Real Estate Practices and Interim Responses to the Survey, 27 N.Y. Real Prop. L.J. 79 (Spring 1999), updated by the Executive Committee in 2002." Karl B. Holtzschue, Holtzschue on Real Estate Contracts and Closings: A Step-by-Step Guide to Buying and Selling Real Estate (Third Edition, 2022).
U.S. Treasuries
Bonds issued directly by the U.S. government. • They are "[g]enerally considered one of the safes assets on the planet." Adam Grealish, Five Places to Put Cash Rather Than in the Bank, Kiplinger, May 1, 2023 (Apple News link).
V
vassal
In feudalism, an individual who swore fealty to a lord.
venue
The place of a trial.
verification
A declaration swearing that the pleadings or statements made in a document are true. NY CPLR 3020(a)defines a verification as a “statement under oath that the pleading is true to the knowledge of the deponent, except as to matters alleged on information and belief, and as to those matters he believes it to be true.”
vest
When a beneficiary meets all of the conditions that are necessary for an interest in trust to take effect. • An unborn beneficiary's interest is always unvested because being born is one of the conditions that are necessary for vesting. • C.f. abeyance.
villein
In thirteenth century England, someone who was a serf, not a slave. A villein had no rights against the villein's lord (other than protection) but had the rights of a free man against third persons. A villein could not leave the manor, which the villein worked for the lord. The villein had a humble dwelling on the manor. The villein's rights were protected only in the manorial courts, not the royal courts. • In fourteenth century England, a villein gradually changed into someone who was a free man whose land holding was fixed by manorial customs and no longer dependent on the lord's will. • This customary tenure eventually became known as "copyhold tenure" because the title to land was recorded on the rolls of the manorial court, and a copy of the rolls was delivered to the tenant. Land held by "copyhold tenure" was transferable only by surrender and admittance, not by the common-law methods of feoffment and grant that were available to free tenants. "The tenant could, by custom, surrender the lands to the lord of the manor to the use of another person designated by the tenant, and the lord was bound to admit such person into the tenancy. The surrender and admittance were recorded on the rolls of the manorial court, and a copy of the rolls were delivered to the new tenant as evidence of his title. Hence, the tenant was said to hold by a copy of court roll, and the form of holding was labeled copyhold tenure." Cornelius J. Moynihan & Sheldon F. Kurtz, Introduction to the Law of Real Property 14 (7th ed. 2020). • The Law of Property Act, 1922, abolished copyhold tenure, as of January 1, 1926, and converted it into free and common socage.
virtual currency
"Virtual currency is defined in Notice 2014-21, 2014-16 I.R.B. 938 (April 14, 2014) (Notice 2014-21 or Notice), for Federal income tax purposes as a digital representation of value that functions as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, or a store of value other than the U.S. dollar or a foreign currency (fiat currency). The Notice provides that convertible virtual currency (that is, virtual currency that has an equivalent value in real currency or that acts as a substitute for real currency) is treated as property for Federal income tax purposes." Gross Proceeds and Basis Reporting by Brokers and Determination of Amount Realized and Basis for Digital Asset Transactions, Proposed Rule by the IRS, Aug. 2023.
vouch to warranty
In feudal times, the ability of a tenant to call in his lord to defend the tenant's title to the land.
virtute officii
Incident to one's office; stemming from one's office. • "All real estate no disposed of by the will descends to the heirs, and many difficult questions of construction formerly arose in deciding whether the title was devised by the will to the executor or whether he had merely a naked power to sell land, the title to which was in the heir or devisee. So also it was frequently important to determine whether the power of sale was a power incident to the office of executor, a power virtute officii, or whether it was a collateral trust." Powers of Sale in an Executor in Pennsylvania.
VIX
See volatility index.
volatility index
"The VIX 'fear' index, a measure of stock market volatility that shoots up when investors grow anxious . . . ." Michael Hiltzik, Column: The Fed's anti-inflation work is almost done, with an assist from the banking crisis, Los Angeles Times, March 22, 2023 (Apple News link).
W
waive extradition
To voluntarily agree to return to another jurisdiction to face criminal charges.
wallet
warrant of eviction
The legal document allowing an eviction to occur.
wardship
In feudal times, when certain tenants (such as those who held by tenure by knight service) died with minor children, the lord became the guardian of both the person and lands of the heir. • "Long after the feudal system lapsed, burdensome feudal landholding rules endured. Particularly resented were . . . the bizarre fiscal exactions, called wardship and marriage, that functioned as penal transfer taxes on minors." John H. Langbein, The Contractarian Basis of the Law of Trusts, 105 Yale L.J. 625 (1995).
wash sale
Selling or trading securities (such as stocks) at a loss, and then buying substantially identical securities within 30 days before or after the date of the sale. • "To prevent investors from gaming the system, the tax code postpones the use of losses if an investor purchases a 'substantially identical' security within 30 days before or after selling the loser. . . . The delayed use of losses applies to wash sales of stocks, bonds, mutual funds and ETFs, among others. It also applies if the investor sells a loser in a taxable account and then buys it in a retirement plan such as an IRA within 30 days. Stock-option grants and exercises also count as purchases." Laura Saunders, The 'You-Make-a-Lot-of-Money Tax' Hits More Americans, WSJ, June 23, 2023 (Apple News link).
waste
A doctrine that limits a life tenant's use of land.
wealth adviser
An ambiguous title that describes someone who does comprehensive planning for a client's wealth, typically a client who is very wealthy. See Alisa Wolfson, Fiduciary vs. financial adviser: What's the difference?, MarketWatch, June 26, 2023.
wealth transfer
The transmission of wealth to others during life (by an outright gift or transfer to a trust) or upon death (by a will trust, will substitute, or operation of law).
wealth-transfer taxes
Estate tax, gift tax, and generation-skipping transfer tax.
WebSurrogate
WebSurrogate provides information on estate proceedings and other filings within New York State Surrogate's Courts. WebSurrogate is a free service that allows you to search files, retrieve documents, and view historical records that are considered to be public information. It provides various search options, such as name, file number, old index, index book pages, and will search. However, WebSurrogate does not provide access to files and documents that are restricted and does not show impounded documents. WebSurrogate only provides links to document images that were filed on or after February 19, 2014. https://websurrogates03.azurewebsites.us/Home/Welcome/
will
"A will is a legal document that states what should happen to your assets when you die and names the person or people in charge of carrying out your wishes." E. Napoletano, What is a will? The estate planning document you need ASAP (even if you think you don't), Fortune, June 19, 2023 (Apple News link). • Historically, a will was an instrument capable of disposing only real property, while a testament related solely to personal property. For this reason, under modern law a will continues to operate as a devise and needs no executor, unless legislature or the testator's will change the default. • New York's EPTL 1-2.19 gives this definition for a will: "(a) A will is an oral declaration or written instrument, made as prescribed by 3-2.1 or 3-2.2 to take effect upon death, whereby a person disposes of property or directs how it shall not be disposed of, disposes of his body or any part thereof, exercises a power, appoints a fiduciary or makes any other provision for the administration of his estate, and which is revocable during his lifetime. (b) Unless the context otherwise requires, the term 'will' includes a 'codicil'." • See executor. C.f. testament.
will substitute
Property that passes on death without a will or the necessity of probate or other court intervention, including joint accounts, lifetime trusts, life insurance, and other accounts with beneficiary designations. Also called "non-probate asset."
woke
(1) Someone who actively focuses on issues of justice (racial and social), the environment, or other societal issues. • "The idea that patriarchy, white supremacy, transphobia, homophobia, Islamophobia, and other ills inexorably saturate our lived realities and that the highest good is to uncover and oppose them is, I think, a central component of 'wokeness' as both its proponents and critics understand it." Thomas Chatterton Williams, You Can't Define Woke, Atlantic, March 17, 2023 (Apple News link).
(2) An adjective that some Republican politicians use to bash any policy that they oppose, specifically one they think is "liberal." It's an appeal to bias as a means to avoid substantive conversation about the particulars of an issue. See, e.g., Sahil Kapur, Josh Hawley labels Silicon Valley Bank 'too woke to fail', NBC News, March 2023 (Apple News link) ("Republicans like Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis and House Oversight Chair James Comer of Kentucky claimed that the bank was too focused on policies around diversity and its consideration of environmental and social factors in investments — known as ESG."); Doyle McManus, Column: Silicon Valley Bank's collapse may be a blessing in disguise, Los Angeles Times, March 19, 2023 (Apple News link) ("Republican politicians provided a dose of comedy, blaming SVB’s financial blunders on the imaginary menace of “woke banking.” There’s no evidence that the bankers’ political leanings, "woke" or otherwise, affected their balance sheet."). • Hani's opinion: Politicians who forestall conversation by using such adjectives get an A+ for rabble-rousing and an F for analysis. For example, to suggest that regulators took over SVB because it is too "woke" overlooks the underlying economics, which Jonathan Weil discusses in his prescient article, Rising Interest Rates Hit Banks' Bond Holdings (WSJ, 11/11/2022, Apple News link), several months before the collapse of SVB: "SVB Financial Group, the parent of Silicon Valley Bank, said the market value of its held-to-maturity bonds was $15.9 billion less than their balance-sheet value, as of Sept. 30. That gap was slightly more than SVB’s $15.8 billion of total equity." See Thomas Chatterton Williams, You Can't Define Woke, Atlantic, March 17, 2023 (Apple News link) ("I have argued for years now that 'woke' is not a viable descriptor for anyone who is critical of the many serious excesses of the left yet remains invested in reaching beyond their own echo chamber. The word is more confusing than useful, and we should make good-faith efforts to avoid using it.").
words of limitation
At common law, words in a conveyance that indicate the estate that has been created. • For example, in the grant "to A and his heirs," the words "and his heirs" are words of limitation. C.f. words of purchase.
words of purchase
At common law, words in a conveyance that identify the grantee. • For example, in the grant "to A and his heirs," "A" is the only word of purchase because it identifies the recipient of the property. C.f. words of limitation.
wrap account
See separately managed account.
X
Y
Z
zakāt
"[A] nearly 1400-year-old wealth tax . . . which is a key component of an Islamic socio-economic system and a main form of worship." Ahmed E. Taha, Reducing the Costs of Zakāt, Pepperdine University Legal Studies Research Paper No. 2022/23, Virginia Tax Review, Vol. 41, No. 2, 2022, Forthcoming (SSRN link).
Hani Sarji
New York lawyer who cares about people, is fascinated by technology, and is writing his next book, Estate of Confusion: New York.




Leave a Comment